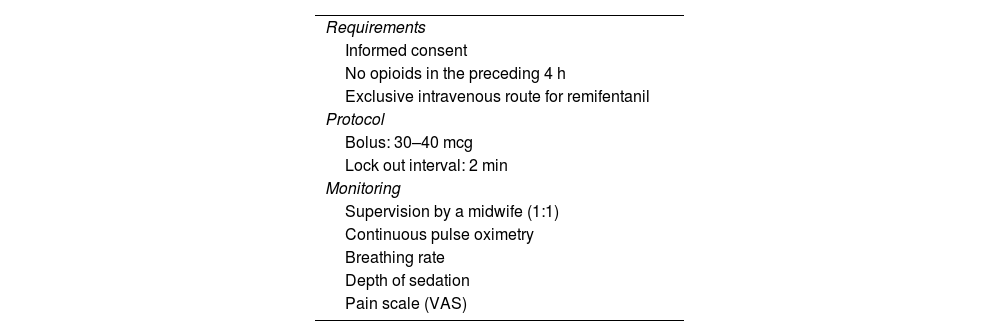
array:23 [ "pii" => "S2341192923001828" "issn" => "23411929" "doi" => "10.1016/j.redare.2023.03.005" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2023-11-01" "aid" => "1501" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Anestesiología, Reanimación y Terapéutica del Dolor" "copyrightAnyo" => "2023" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Revista Española de Anestesiología y Reanimación (English Version). 2023;70:487-90" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S0034935623001305" "issn" => "00349356" "doi" => "10.1016/j.redar.2023.03.002" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2023-11-01" "aid" => "1501" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Anestesiología, Reanimación y Terapéutica del Dolor" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "sco" "cita" => "Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim. 2023;70:487-90" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "es" => array:9 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Editorial</span>" "titulo" => "Remifentanilo intravenoso para analgesia en el dolor del trabajo de parto: ¿es eficaz, seguro y factible?" "tienePdf" => "es" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "es" "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "487" "paginaFinal" => "490" ] ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "es" => true ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "E. Guasch Arévalo, N. Brogly" "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "E." "apellidos" => "Guasch Arévalo" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "N." "apellidos" => "Brogly" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "en" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S2341192923001828" "doi" => "10.1016/j.redare.2023.03.005" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2341192923001828?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0034935623001305?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/00349356/0000007000000009/v1_202310300651/S0034935623001305/v1_202310300651/es/main.assets" ] ] "itemSiguiente" => array:19 [ "pii" => "S2341192923001452" "issn" => "23411929" "doi" => "10.1016/j.redare.2023.09.002" "estado" => "S300" "fechaPublicacion" => "2023-11-01" "aid" => "1499" "copyright" => "Sociedad Española de Anestesiología, Reanimación y Terapéutica del Dolor" "documento" => "article" "crossmark" => 1 "subdocumento" => "fla" "cita" => "Revista Española de Anestesiología y Reanimación (English Version). 2023;70:491-500" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "en" => array:13 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Original article</span>" "titulo" => "Role of protocol-guided perioperative care to enhance recovery after head and neck neoplasm surgery: An institutional experience" "tienePdf" => "en" "tieneTextoCompleto" => "en" "tieneResumen" => array:2 [ 0 => "en" 1 => "es" ] "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "491" "paginaFinal" => "500" ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Rol de los cuidados perioperatorios guiados por protocolo para mejorar la recuperación tras la cirugía de cáncer de cabeza y cuello: experiencia institucional" ] ] "contieneResumen" => array:2 [ "en" => true "es" => true ] "contieneTextoCompleto" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "contienePdf" => array:1 [ "en" => true ] "resumenGrafico" => array:2 [ "original" => 0 "multimedia" => array:8 [ "identificador" => "fig0010" "etiqueta" => "Figure 2" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIAFIGURA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "figura" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "imagen" => "gr2.jpeg" "Alto" => 919 "Ancho" => 2091 "Tamanyo" => 123790 ] ] "detalles" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "at0010" "detalle" => "Figure " "rol" => "short" ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Comparison of time to readiness for discharge and length of stay between groups using the median test for independent sample (Mann–Whitney <span class="elsevierStyleItalic">U</span> test).</p>" ] ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "autoresLista" => "N. Govil, M. Tripathi, K. Parag, S.P. Agrawal, M. Kumar, S. Varshney" "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "N." "apellidos" => "Govil" ] 1 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "M." "apellidos" => "Tripathi" ] 2 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "K." "apellidos" => "Parag" ] 3 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "S.P." "apellidos" => "Agrawal" ] 4 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "M." "apellidos" => "Kumar" ] 5 => array:2 [ "nombre" => "S." "apellidos" => "Varshney" ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "Traduccion" => array:1 [ "es" => array:9 [ "pii" => "S0034935623001287" "doi" => "10.1016/j.redar.2022.10.003" "estado" => "S300" "subdocumento" => "" "abierto" => array:3 [ "ES" => false "ES2" => false "LATM" => false ] "gratuito" => false "lecturas" => array:1 [ "total" => 0 ] "idiomaDefecto" => "es" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S0034935623001287?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ] ] "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2341192923001452?idApp=UINPBA00004N" "url" => "/23411929/0000007000000009/v1_202311162251/S2341192923001452/v1_202311162251/en/main.assets" ] "en" => array:15 [ "idiomaDefecto" => true "cabecera" => "<span class="elsevierStyleTextfn">Editorial article</span>" "titulo" => "Intravenous remifentanil for labour analgesia: is it effective, safe, and feasible?" "tieneTextoCompleto" => true "paginas" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "paginaInicial" => "487" "paginaFinal" => "490" ] ] "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:4 [ "autoresLista" => "E. Guasch Arévalo, N. Brogly" "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => array:4 [ "nombre" => "E." "apellidos" => "Guasch Arévalo" "email" => array:1 [ 0 => "emiguasch@hotmail.com" ] "referencia" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">a</span>" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">*</span>" "identificador" => "cor0005" ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "nombre" => "N." "apellidos" => "Brogly" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etiqueta" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSup">b</span>" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] ] ] ] "afiliaciones" => array:2 [ 0 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Sección Anestesia-Reanimación Obstétrica, Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid; Comité de Anestesia Obstétrica de la Federación Mundial de Sociedades de Anestesia (WFSA); Board Europeo de Anestesia de la Unión Europea de Médicos Especialistas (EBA-UEMS); Board y Council WFSA, Spain" "etiqueta" => "a" "identificador" => "aff0005" ] 1 => array:3 [ "entidad" => "Servicio Anestesia-Reanimación, Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid; Servicio de Anestesia, Hospital Universitario La Zarzuela; Madrid; Sección de Anestesia Obstétrica de la Sociedad Española de Anestesia-Reanimación (SEDAR); Subforum de Anestesia obstétrica Sociedad Europea de Anestesia y Cuidados Intensivos (ESAIC); Chair SubComité Parte 1 del Diploma Europeo Anestesia y Cuidados intensivos (EDAIC part 1) de la Sociedad Europea de Anestesia y Cuidados Intensivos (ESAIC), Spain" "etiqueta" => "b" "identificador" => "aff0010" ] ] "correspondencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "cor0005" "etiqueta" => "⁎" "correspondencia" => "Corresponding author." ] ] ] ] "titulosAlternativos" => array:1 [ "es" => array:1 [ "titulo" => "Remifentanilo intravenoso para analgesia en el dolor del trabajo de parto: ¿es eficaz, seguro y factible?" ] ] "textoCompleto" => "<span class="elsevierStyleSections"><p id="par0005" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">In recent years, the demand for labour analgesia has become widespread, given that pain control and quality of life are priorities for both women and the doctors who treat them.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0005"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">1</span></a> In Spain, neuraxial analgesia in any of its variants (epidural, intradural, or combined) is the most widely used analgesic modality - possibly because its efficacy-safety balance is superior to all other options - and it is now considered the gold-standard in this context.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0010"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">2</span></a> Some women, however, are not candidates for neuraxial analgesia due to medical contraindication or other reasons, and can be offered other, albeit less effective, analgesic modalities to alleviate labour pain. One such option is patient controlled analgesia with intravenous remifentanil (rPCA).</p><p id="par0010" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">The use of remifentanil in PCA for labour pain has been documented since 2000.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0015"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">3</span></a> Remifentanil is a μ opioid receptor agonist with a latency of 30−60 s and a peak effect at 2.5 min.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0020"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">4</span></a> It is rapidly metabolized by plasma esterases and has a very short context-sensitive half-life (T<span class="elsevierStyleInf">1/2</span> α: 0.5–1.5 min, T<span class="elsevierStyleInf">1/2</span> β: 5−8 min).<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0025"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">5–7</span></a> It has no cumulative effect in infusion, can be administered over long periods, and is eliminated within 3−10 min regardless of the duration of treatment.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0040"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">8</span></a> Remifentanil can be maintained throughout the cervical dilation phase until delivery.</p><p id="par0015" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">These characteristics give the drug several potential advantages for women in labour. However, the pain of uterine contractions is intermittent, and with rPCA pain control is delayed by 10–20 s.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0045"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">9</span></a></p><p id="par0020" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">A recent meta-analysis<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0050"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">10</span></a> of 10 randomized clinical trials found no differences between rPCA and epidural analgesia in terms of foetal impact (Apgar score <7 at 5 min of life) and patient satisfaction; however, rPCA appears to be associated with a lower incidence of intrapartum fever, and a significantly higher incidence of maternal respiratory depression. Pain control with rPCA is rapid and does not appear to affect the duration of the first or second phase of labour or the incidence of caesarean section.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0055"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">11–15</span></a> There are no data on complications, such as a higher or lower incidence of uterine atony and postpartum haemorrhage.</p><p id="par0025" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Several studies indicate that, although remifentanil easily and quickly passes through the placental barrier, its effect on neonatal respiratory depression is insignificant due to its rapid metabolism.</p><p id="par0030" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Let us briefly analyse the 3 factors that have motivated this editorial: efficacy, safety, and resource management.</p><span id="sec0005" class="elsevierStyleSection elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSectionTitle" id="sect0005">Efficacy</span><p id="par0035" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">The use of rPCA has been compared with meperidine and neuraxial analgesia. The RESPITE study<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0080"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">16</span></a> compares rPCA with intramuscular meperidine. The efficacy results were inconclusive, although the fact that many women (>60%) refused to participate in the study shows a clear preference for neuraxial analgesia.</p><p id="par0040" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">A recently created, continuously updated registry of cases in which rPCA was administered and any side effects observed<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0085"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">17,18</span></a> brings together data from 31 European countries regarding the efficacy and serious side effects of rPCA for labour pain. An audit of 5,740 cases registered between 2010 and 2015 showed that 27.3% of women presented episodes of hypoxia (oxygen saturation <94%), 25.8% presented sedation, 16.9% nausea and vomiting, 2.8% presented pruritus, and neonatal resuscitation was required in 0.3% of cases. No serious complications, defined as a respiratory depression requiring assisted ventilation or a cardiac arrest, were recorded if the number of cases per centre exceeded 10 per year.</p><p id="par0045" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">In Northern Ireland, rPCA was the most widely used analgesia modality between 2005 and 2014 (8170/25,617 women analysed), and was associated with an incidence of instrumental delivery or caesarean section similar to that observed in patients receiving epidural analgesia, with no differences in neonatal outcomes. Onset of maternal respiratory depression was rapidly diagnosed thanks to the constant presence of a midwife.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0095"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">19</span></a></p></span><span id="sec0010" class="elsevierStyleSection elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSectionTitle" id="sect0010">Safety</span><p id="par0050" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">The side effects described are: hypoxia,<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0100"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">20,21</span></a> cardiac and respiratory arrest,<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0110"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">22,23</span></a> pruritus, nausea and vomiting.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0100"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">20</span></a> The most reliable data come from the aforementioned database.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0085"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">17,18</span></a> It is important the bear in mind that in terms of safety, continuous monitoring does not replace surveillance, and that the use of capnography does not exclude the possibility of maternal respiratory depression. According to Logtenberg et al. who performed a large study in the Netherlands, maternal monitoring is essential to avoid complications<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0110"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">22</span></a> - an observation corroborated by Tveit et al. in their prospective study.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0105"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">21</span></a></p></span><span id="sec0015" class="elsevierStyleSection elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSectionTitle" id="sect0015">Human and materials resources</span><p id="par0055" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Providing women in labour with analgesia on demand should be considered a human right. However, before offering a specific analgesic modality, such as neuraxial analgesia or rPCA, the attending clinician must weigh up the advantages, disadvantages and possible complications, taking into account the hospital’s infrastructure, staff, and their competence to deal with such complications. These requirements are shown in <a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#tbl0005">Table 1</a>.</p><elsevierMultimedia ident="tbl0005"></elsevierMultimedia><p id="par0060" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">In terms of staffing, a 1:1 midwife-patient ratio is recommended, although this is not always easy to achieve.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0120"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">24</span></a> The difficulty of providing adequate nurse follow-up is further complicated by major fluctuations in the number of births over a given period and the difficulty of increasing staff numbers in parallel with these trends. Respiratory monitoring alone, including capnography, does not replace the presence of a trained healthcare professional. These are the issues that currently limit the widespread use of rPCA as a routine labour analgesia option, and alternative analgesic options are required.</p><p id="par0065" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">According to the recommendations of the Royal College of Anaesthesiologists,<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0125"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">25</span></a> units that provide rPCA for labour analgesia should have local policies and processes in place to ensure that it is used safely, that midwives who care for women using rPCA are familiar with its use and have received specific training. Unit staffing levels should permit continuous midwifery supervision of its use.</p><p id="par0070" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">Some protocols clearly specify that the midwife should not leave the dilation room once rPCA has begun.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0130"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">26</span></a></p><p id="par0075" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">The need for maternal respiratory monitoring is an obstacle to widespread implementation of rPCA as an analgesic modality.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0080"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">16,27</span></a> Current guidelines recommend monitoring maternal status with electrocardiography and continuous pulse oximetry, implementing measures to prevent or facilitate prompt diagnosis of respiratory depression during rPCA, and providing resources for immediate maternal and neonatal resuscitation in order to improve prognosis if complications occur.</p><p id="par0080" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">In conclusion, we summarize the SEDAR recommendations,<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRefs" href="#bib0140"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">28–30</span></a> including the requirements, protocol, indications and contraindications of rPCA.<ul class="elsevierStyleList" id="lis0005"><li class="elsevierStyleListItem" id="lsti0005"><span class="elsevierStyleLabel">-</span><p id="par0085" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">“Remifentanil is a moderately effective analgesic alternative, although it is associated with certain risks. It must be used with strict safety protocols."<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0140"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">28</span></a> (<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#tbl0005">Table 1</a>).</p></li><li class="elsevierStyleListItem" id="lsti0010"><span class="elsevierStyleLabel">-</span><p id="par0090" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">“Continuous one-to-one monitoring by a healthcare professional is essential when using rPCA, since respiratory depression can occur at any time after the start of opioid analgesia. Respiratory rate, depth of sedation, and pain should be assessed at regular intervals, and the foetal heart rate should be monitored continuously”.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0145"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">29</span></a></p></li><li class="elsevierStyleListItem" id="lsti0015"><span class="elsevierStyleLabel">-</span><p id="par0095" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">“When using rPCA, SaO<span class="elsevierStyleInf">2</span>, respiratory rate and depth of sedation should be monitored, the patient should be given supplementary oxygen and be monitored continuously by a midwife (one-to-one)”.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0150"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">30</span></a></p></li><li class="elsevierStyleListItem" id="lsti0020"><span class="elsevierStyleLabel">-</span><p id="par0100" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">"The healthcare system must be flexible enough to offer this and other analgesic alternatives safely and effectively when demanded or required by the patient."</p></li></ul></p></span><span id="sec0020" class="elsevierStyleSection elsevierViewall"><span class="elsevierStyleSectionTitle" id="sect0020">Conflict of interests</span><p id="par0105" class="elsevierStylePara elsevierViewall">None.</p></span></span>" "textoCompletoSecciones" => array:1 [ "secciones" => array:5 [ 0 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "sec0005" "titulo" => "Efficacy" ] 1 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "sec0010" "titulo" => "Safety" ] 2 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "sec0015" "titulo" => "Human and materials resources" ] 3 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "sec0020" "titulo" => "Conflict of interests" ] 4 => array:1 [ "titulo" => "References" ] ] ] "pdfFichero" => "main.pdf" "tienePdf" => true "fechaRecibido" => "2023-01-10" "fechaAceptado" => "2023-03-01" "multimedia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:8 [ "identificador" => "tbl0005" "etiqueta" => "Table 1" "tipo" => "MULTIMEDIATABLA" "mostrarFloat" => true "mostrarDisplay" => false "detalles" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "at0005" "detalle" => "Table " "rol" => "short" ] ] "tabla" => array:2 [ "leyenda" => "<p id="spar0010" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">From Pérez-Pardo and Suárez-Castaños.<a class="elsevierStyleCrossRef" href="#bib0140"><span class="elsevierStyleSup">28</span></a></p>" "tablatextoimagen" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "tabla" => array:1 [ 0 => """ <table border="0" frame="\n \t\t\t\t\tvoid\n \t\t\t\t" class=""><tbody title="tbody"><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleItalic">Requirements</span> \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>Informed consent \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>No opioids in the preceding 4 h \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>Exclusive intravenous route for remifentanil \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleItalic">Protocol</span> \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>Bolus: 30–40 mcg \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>Lock out interval: 2 min \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleItalic">Monitoring</span> \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>Supervision by a midwife (1:1) \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>Continuous pulse oximetry \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>Breathing rate \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>Depth of sedation \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr><tr title="table-row"><td class="td-with-role" title="\n \t\t\t\t\ttable-entry\n \t\t\t\t ; entry_with_role_rowhead " align="left" valign="\n \t\t\t\t\ttop\n \t\t\t\t"><span class="elsevierStyleHsp" style=""></span>Pain scale (VAS) \t\t\t\t\t\t\n \t\t\t\t</td></tr></tbody></table> """ ] "imagenFichero" => array:1 [ 0 => "xTab3338586.png" ] ] ] ] "descripcion" => array:1 [ "en" => "<p id="spar0005" class="elsevierStyleSimplePara elsevierViewall">Recommendations for remifentanil use.</p>" ] ] ] "bibliografia" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "References" "seccion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "identificador" => "bibs0005" "bibliografiaReferencia" => array:30 [ 0 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0005" "etiqueta" => "1" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "COVID in obstetrics: labor analgesia and cesarean section" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => "E. Guasch" 1 => "N. Brogly" 2 => "F. Gilsanz" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1097/ACO.0000000000000949" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "Curr Opin Anaesthesiol" "fecha" => "2021" "volumen" => "34" "numero" => "1" "paginaInicial" => "62" "paginaFinal" => "68" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33315638" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 1 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0010" "etiqueta" => "2" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Update on non-neuraxial labor analgesia" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => "D. Karol" 1 => "C.F. Weiniger" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1007/s40140-021-00463-4" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Curr Anesthesiol Rep" "fecha" => "2021" "volumen" => "11" "numero" => "3" "paginaInicial" => "348" "paginaFinal" => "354" ] ] ] ] ] ] 2 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0015" "etiqueta" => "3" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Remifentanil for labor analgesia: a comprehensive review" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => "Y. Ohashi" 1 => "L. Baghirzada" 2 => "H. Sumikura" 3 => "M. Balki" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1007/s00540-016-2233-y" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "J Anesth" "fecha" => "2016" "volumen" => "30" "numero" => "6" "paginaInicial" => "1020" "paginaFinal" => "1030" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27619509" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 3 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0020" "etiqueta" => "4" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Patient satisfaction between remifentanil patient-controlled analgesia and epidural analgesia for labor pain" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "S. Frauenfelder" 1 => "R. van Rijn" 2 => "C.M. Radder" 3 => "M.C. de Vries" 4 => "L.M. Dijksman" 5 => "M.B. Godfried" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1111/aogs.12694" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand" "fecha" => "2015" "volumen" => "94" "numero" => "9" "paginaInicial" => "1014" "paginaFinal" => "1021" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26073456" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 4 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0025" "etiqueta" => "5" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Remifentanil as an alternative to epidural analgesia for vaginal delivery: a meta-analysis of randomized trials" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "M. Lee" 1 => "F. Zhu" 2 => "J. Moodie" 3 => "Z. Zhang" 4 => "D. Cheng" 5 => "J. Martin" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1016/j.jclinane.2017.03.026" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "J Clin Anesth" "fecha" => "2017" "volumen" => "39" "paginaInicial" => "57" "paginaFinal" => "63" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28494909" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 5 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0030" "etiqueta" => "6" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Analgesic efficacy of remifentanil patient-controlled analgesia versus combined spinal-epidural technique in multiparous women during labour" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "I. Blajic" 1 => "T. Zagar" 2 => "N. Semrl" 3 => "N. Umek" 4 => "M. Lucovnik" 5 => "T. Stopar Pintaric" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.5603/GP.a2021.0053" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "Ginekol Pol" "fecha" => "2021" "volumen" => "92" "numero" => "11" "paginaInicial" => "797" "paginaFinal" => "803" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33914329" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 6 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0035" "etiqueta" => "7" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Remifentanil patient-controlled analgesia following cardiac surgery" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => "K. Krishnan" 1 => "S.C. Elliot" 2 => "J.C. Berridge" 3 => "A. Mallick" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1111/j.1399-6576" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "Acta Anaesthesiol Scand" "fecha" => "2005" "volumen" => "49" "numero" => "6" "paginaInicial" => "876" "paginaFinal" => "879" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15954975" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 7 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0040" "etiqueta" => "8" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Photoplethysmography-derived approximate entropy and sample entropy as measures of analgesia depth during propofol-remifentanil anesthesia" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "W. Chen" 1 => "F. Jiang" 2 => "X. Chen" 3 => "Y. Feng" 4 => "J. Miao" 5 => "S. Chen" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1007/s10877-020-00470-6" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "J Clin Monit Comput" "fecha" => "2021" "volumen" => "35" "numero" => "2" "paginaInicial" => "297" "paginaFinal" => "305" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32026257" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 8 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0045" "etiqueta" => "9" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Curative effect of remifentanil on labor analgesia in newborns" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => "Z. Jia" 1 => "Y. Li" 2 => "H. Jia" 3 => "J. Ren" 4 => "N. Xie" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1080/14767058.2018.1533946" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med" "fecha" => "2020" "volumen" => "33" "numero" => "11" "paginaInicial" => "1913" "paginaFinal" => "1918" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30849250" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 9 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0050" "etiqueta" => "10" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "The efficacy and safety of remifentanil patient-controlled versus epidural analgesia in labor: a meta-analysis and systematic review" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "X. Lei" 1 => "Y. Yu" 2 => "M. Li" 3 => "P. Fang" 4 => "S. Gan" 5 => "Y. Yao" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:2 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:4 [ "tituloSerie" => "PLoS One" "fecha" => "2022" "volumen" => "17" "numero" => "12" ] ] 1 => array:1 [ "WWW" => array:1 [ "link" => "https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0275716" ] ] ] ] ] ] 10 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0055" "etiqueta" => "11" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Remifentanil patient-controlled versus epidural analgesia on intrapartum maternal fever: a systematic review and meta-analysis" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => "G. Lu" 1 => "W. Yao" 2 => "X. Chen" 3 => "S. Zhang" 4 => "M. Zhou" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1186/s12884-020-2800-y" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "BMC Pregnancy Childbirth" "fecha" => "2020" "volumen" => "20" "numero" => "1" "paginaInicial" => "151" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32164593" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 11 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0060" "etiqueta" => "12" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Effect and safety of remifentanil patient-controlled analgesia compared with epidural analgesia in labor: an updated meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => "P. Zhang" 1 => "Z. Yu" 2 => "M. Zhai" 3 => "J. Cui" 4 => "J. Wang" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1159/000515531" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Gynecol Obstet Invest" "fecha" => "2021" "volumen" => "86" "numero" => "3" "paginaInicial" => "231" "paginaFinal" => "238" ] ] ] ] ] ] 12 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0065" "etiqueta" => "13" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Patient-controlled analgesia with remifentanil versus alternative parenteral methods for pain management in labour" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "S. Weibel" 1 => "Y. Jelting" 2 => "A. Afshari" 3 => "N.L. Pace" 4 => "L.H. Eberhart" 5 => "J. Jokinen" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1002/14651858.CD011989.pub2" "Revista" => array:3 [ "tituloSerie" => "Cochrane Database Syst Rev" "fecha" => "2017" "volumen" => "4" ] ] ] ] ] ] 13 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0070" "etiqueta" => "14" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Remifentanil tolerance and hyperalgesia: short-term gain, longterm pain?" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => "E.H. Yu" 1 => "D.H. Tran" 2 => "S.W. Lam" 3 => "M.G. Irwin" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1111/anae.13602" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "Anaesthesia" "fecha" => "2016" "volumen" => "71" "numero" => "11" "paginaInicial" => "1347" "paginaFinal" => "1362" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27734470" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 14 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0075" "etiqueta" => "15" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Intraoperative remifentanil dosage in surgery for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis does not increase postoperative opioid consumption when combined with epidural analgesia: a retrospective cohort study" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "Y. Aoki" 1 => "H. Iwata" 2 => "C. Akinaga" 3 => "Y. Shiko" 4 => "Y. Kawasaki" 5 => "K. Kobayashi" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.7759/cureus.17361" "Revista" => array:4 [ "tituloSerie" => "Cureus" "fecha" => "2021" "volumen" => "13" "numero" => "8" ] ] ] ] ] ] 15 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0080" "etiqueta" => "16" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Intravenous remifentanil patient-controlled analgesia versus intramuscular pethidine for pain relief in labour (RESPITE): an open-label, multicentre, randomised controlled trial" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:3 [ "colaboracion" => "RESPITE Trial Collaborative Group." "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "M.J.A. Wilson" 1 => "C. MacArthur" 2 => "C.A. Hewitt" 3 => "K. Handley" 4 => "F. Gao" 5 => "L. Beeson" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31613-1" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "Lancet." "fecha" => "2018" "volumen" => "392" "numero" => "10148" "paginaInicial" => "662" "paginaFinal" => "672" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30115484" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 16 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0085" "etiqueta" => "17" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "referenciaCompleta" => "<a target="_blank" href="https://www.remipca.org/php/en/index.php">https://www.remipca.org/php/en/index.php</a>. (Consultado el 6/01/2022)." ] ] ] 17 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0090" "etiqueta" => "18" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Remifentanil patient-controlled analgesia in labour: six-year audit of outcome data of the RemiPCA SAFE Network (2010–2015)" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "A.A. Melber" 1 => "Y. Jelting" 2 => "M. Huber" 3 => "D. Keller" 4 => "A. Dullenkopf" 5 => "T. Girard" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1016/j.ijoa.2018.12.004" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Int J Obstet Anesth" "fecha" => "2019" "volumen" => "39" "paginaInicial" => "12" "paginaFinal" => "21" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30685299" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 18 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0095" "etiqueta" => "19" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Remifentanil patient controlled intravenous analgesia during labour: a retrospective observational study of 10 years’ experience" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => "H. Murray" 1 => "P. Hodgkinson" 2 => "D. Hughes" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1016/j.ijoa.2019.05.012" "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Int J Obstet Anesth" "fecha" => "2019" "volumen" => "39" "paginaInicial" => "29" "paginaFinal" => "34" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31230993" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 19 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0100" "etiqueta" => "20" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "A randomized controlled trial of the efficacy and respiratory effects of patient-controlled intravenous remifentanil analgesia and patient-controlled epidural analgesia in laboring women" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "D. Stocki" 1 => "I. Matot" 2 => "S. Einav" 3 => "S. Eventov-Friedman" 4 => "Y. Ginosar" 5 => "C.F. Weiniger" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182a7cd1b" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "Anesth Analg." "fecha" => "2014" "volumen" => "118" "numero" => "3" "paginaInicial" => "589" "paginaFinal" => "597" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24149580" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 20 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0105" "etiqueta" => "21" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Efficacy and side effects of intravenous remifentanil patient-controlled analgesia used in a stepwise approach for labour: an observational study" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:4 [ 0 => "T.O. Tveit" 1 => "A. Halvorsen" 2 => "S. Seiler" 3 => "J.H. Rosland" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1016/j.ijoa.2012.09.003" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "Int J Obstet Anesth" "fecha" => "2013" "volumen" => "22" "numero" => "1" "paginaInicial" => "19" "paginaFinal" => "25" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23151415" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 21 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0110" "etiqueta" => "22" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Pharmacological pain relief and fear of childbirth in low risk women; secondary analysis of the RAVEL study" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => true "autores" => array:6 [ 0 => "S.L. Logtenberg" 1 => "C.J. Verhoeven" 2 => "K.O. Rengerink" 3 => "A.M. Sluijs" 4 => "L.M. Freeman" 5 => "F.G. Schellevis" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1186/s12884-017-1633-9" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "BMC Pregnancy Childbirth" "fecha" => "2018" "volumen" => "18" "numero" => "1" "paginaInicial" => "1" "paginaFinal" => "9" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29291732" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 22 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0115" "etiqueta" => "23" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "A survey of intravenous remifentanil use for labor analgesia at academic medical centers in the United States" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:5 [ 0 => "J. Aaronson" 1 => "S. Abramovitz" 2 => "R. Smiley" 3 => "V. Tangel" 4 => "R. Landau" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "Revista" => array:6 [ "tituloSerie" => "Anesth Analg." "fecha" => "2017" "volumen" => "124" "numero" => "4" "paginaInicial" => "1208" "paginaFinal" => "1210" ] ] ] ] ] ] 23 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0120" "etiqueta" => "24" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Non-regional analgesia for labour: remifentanil in obstetrics" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => "I. Ronel" 1 => "C.F. Weiniger" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1016/j.bjae.2019.07.002" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "BJA Educ." "fecha" => "2019" "volumen" => "19" "numero" => "11" "paginaInicial" => "357" "paginaFinal" => "361" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/33456858" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] 24 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0125" "etiqueta" => "25" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "referenciaCompleta" => "<a target="_blank" href="https://www.rcoa.ac.uk/gpas/chapter-9#rec-14706">https://www.rcoa.ac.uk/gpas/chapter-9#rec-14706</a> (Consultado el 6/01/2022)." ] ] ] 25 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0130" "etiqueta" => "26" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "referenciaCompleta" => "<a target="_blank" href="https://www.oaa-anaes.ac.uk/assets/_managed/cms/files/Clinical%20Guidelines/Remifentanil_Dudley_2013.pdf">https://www.oaa-anaes.ac.uk/assets/_managed/cms/files/Clinical%20Guidelines/Remifentanil_Dudley_2013.pdf</a><a target="_blank" href="https://mft.nhs.uk/app/uploads/sites/4/2018/04/Remifentanil-PCA-for-Women-in-Labour-October-2017.pdf">https://mft.nhs.uk/app/uploads/sites/4/2018/04/Remifentanil-PCA-for-Women-in-Labour-October-2017.pdf</a> (Consultado el 6/01/2022)." ] ] ] 26 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0135" "etiqueta" => "27" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Remifentanil patient-controlled analgesia for labour: a complete audit cycle" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:3 [ 0 => "U. Buehner" 1 => "J.R. Broadbent" 2 => "B. Chesterfield" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:2 [ 0 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1177/0310057X1103900421" "Revista" => array:7 [ "tituloSerie" => "Anaesth Intensive Care" "fecha" => "2011" "volumen" => "39" "numero" => "4" "paginaInicial" => "666" "paginaFinal" => "670" "link" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "url" => "https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21823387" "web" => "Medline" ] ] ] ] 1 => array:2 [ "doi" => "10.1177/0310057X1103900421" "WWW" => array:1 [ "link" => "https://doi.org/10.1177/0310057X1103900421" ] ] ] ] ] ] 27 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0140" "etiqueta" => "28" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Recommendaciones actuales en analgesia para el trabajo de parto" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => "O. Pérez-Pardo" 1 => "C. Suárez-Castaños" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "LibroEditado" => array:6 [ "editores" => "N.Brogly, S.Manrique, E.Guasch" "titulo" => "Protocolos asistenciales de la sección de anestesia obstétrica de la SEDAR" "paginaInicial" => "101" "paginaFinal" => "117" "edicion" => "3º edición" "serieFecha" => "2021" ] ] ] ] ] ] 28 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0145" "etiqueta" => "29" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Recommendaciones anestésicas en los partos de bajo riesgo" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => "A. Schyns-van-den-Berg" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "LibroEditado" => array:6 [ "editores" => "N.Brogly, S.Manrique, E.Guasch" "titulo" => "Protocolos asistenciales de la sección de anestesia obstétrica de la SEDAR" "paginaInicial" => "119" "paginaFinal" => "129" "edicion" => "3º edición" "serieFecha" => "2021" ] ] ] ] ] ] 29 => array:3 [ "identificador" => "bib0150" "etiqueta" => "30" "referencia" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "contribucion" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Alternativas farmacológicas y no farmacológicas a la epidural. Parto fisiológico" "autores" => array:1 [ 0 => array:2 [ "etal" => false "autores" => array:2 [ 0 => "L. Hernández-González" 1 => "R. Sánchez-Nuez" ] ] ] ] ] "host" => array:1 [ 0 => array:1 [ "LibroEditado" => array:6 [ "editores" => "N.Brogly, S.Manrique, E.Guasch" "titulo" => "Protocolos asistenciales de la sección de anestesia obstétrica de la SEDAR" "paginaInicial" => "147" "paginaFinal" => "158" "edicion" => "3º edición" "serieFecha" => "2021" ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" "url" => "/23411929/0000007000000009/v1_202311162251/S2341192923001828/v1_202311162251/en/main.assets" "Apartado" => array:4 [ "identificador" => "62207" "tipo" => "SECCION" "en" => array:2 [ "titulo" => "Editorial article" "idiomaDefecto" => true ] "idiomaDefecto" => "en" ] "PDF" => "https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/23411929/0000007000000009/v1_202311162251/S2341192923001828/v1_202311162251/en/main.pdf?idApp=UINPBA00004N&text.app=https://www.elsevier.es/" "EPUB" => "https://multimedia.elsevier.es/PublicationsMultimediaV1/item/epub/S2341192923001828?idApp=UINPBA00004N" ]
Journal Information
Vol. 70. Issue 9.
Pages 487-490 (November 2023)
Share
Download PDF
More article options
Vol. 70. Issue 9.
Pages 487-490 (November 2023)
Editorial article
Intravenous remifentanil for labour analgesia: is it effective, safe, and feasible?
Remifentanilo intravenoso para analgesia en el dolor del trabajo de parto: ¿es eficaz, seguro y factible?
Visits
3
a Sección Anestesia-Reanimación Obstétrica, Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid; Comité de Anestesia Obstétrica de la Federación Mundial de Sociedades de Anestesia (WFSA); Board Europeo de Anestesia de la Unión Europea de Médicos Especialistas (EBA-UEMS); Board y Council WFSA, Spain
b Servicio Anestesia-Reanimación, Hospital Universitario La Paz, Madrid; Servicio de Anestesia, Hospital Universitario La Zarzuela; Madrid; Sección de Anestesia Obstétrica de la Sociedad Española de Anestesia-Reanimación (SEDAR); Subforum de Anestesia obstétrica Sociedad Europea de Anestesia y Cuidados Intensivos (ESAIC); Chair SubComité Parte 1 del Diploma Europeo Anestesia y Cuidados intensivos (EDAIC part 1) de la Sociedad Europea de Anestesia y Cuidados Intensivos (ESAIC), Spain
This item has received
Article information
These are the options to access the full texts of the publication Revista Española de Anestesiología y Reanimación (English Edition)
Subscriber
Subscribe
Purchase
Contact
Phone for subscriptions and reporting of errors
From Monday to Friday from 9 a.m. to 6 p.m. (GMT + 1) except for the months of July and August which will be from 9 a.m. to 3 p.m.
Calls from Spain
932 415 960
Calls from outside Spain
+34 932 415 960
E-mail