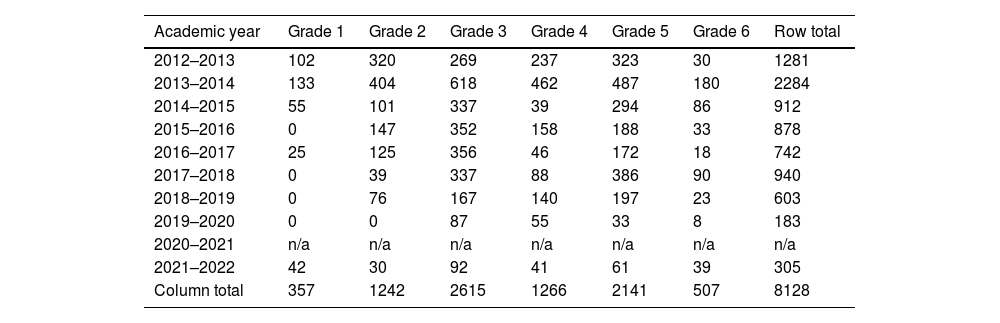
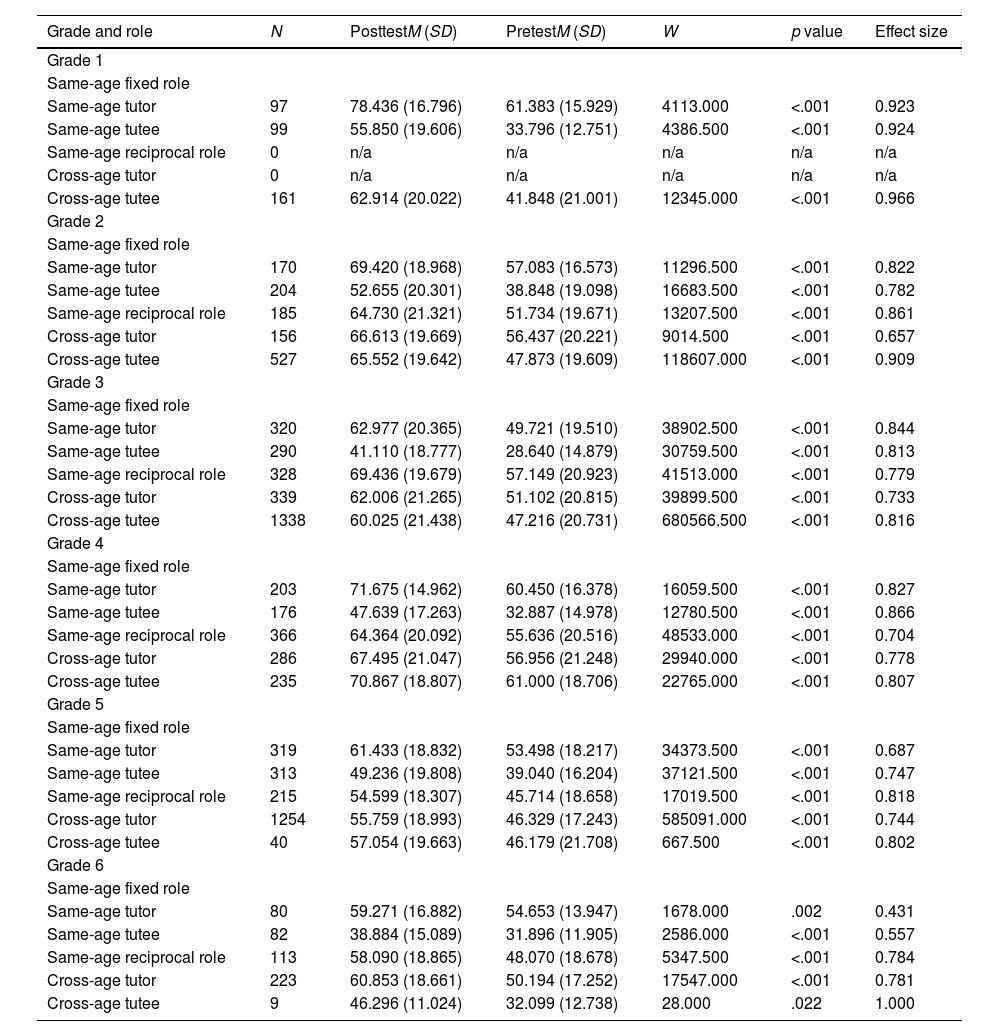
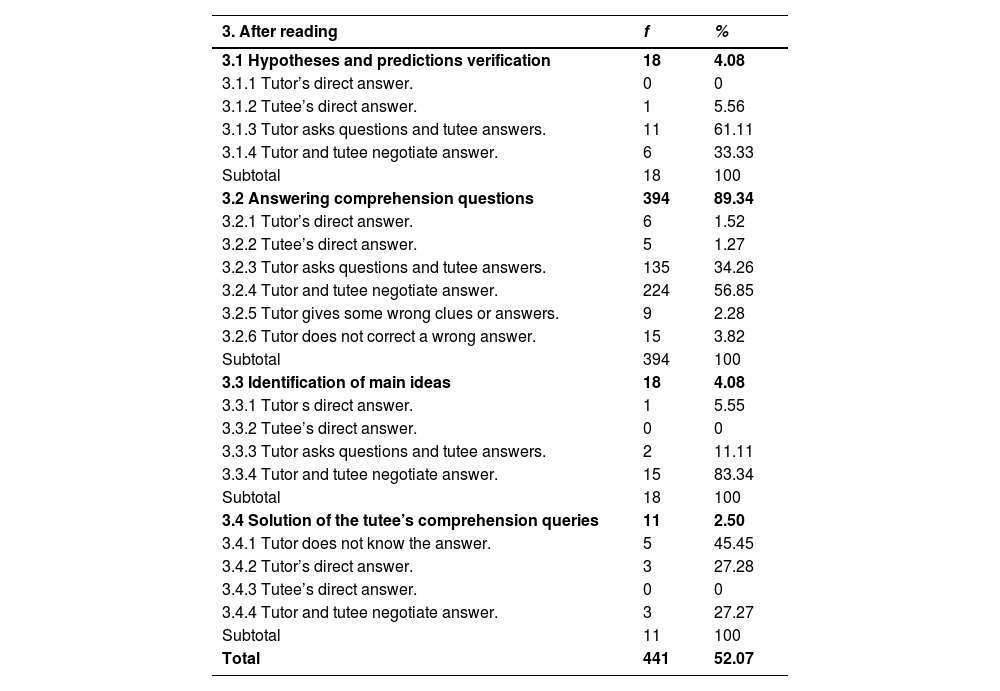
This study investigates the development of reading comprehension in primary school students who took part in a peer tutoring programme. Data were collected from 8,128 students (aged 6–12) from 58 schools that participated in the programme between 2012 and 2022. Adopting a mixed-methods sequential explanatory design, two research aims are addressed: (1) to detect changes in reading comprehension in a pretest-posttest, and (2) to analyse the interaction of a subsample of pairs to explain these changes. Pretest-posttest subgroup analyses show a significant improvement in reading comprehension for all levels, tutoring options, and roles (i.e., same-age tutors and tutees, same-age reciprocal role, cross-age tutors and tutees) (.43 ≤ ES ≤ .97). A linear mixed model shows that grade level and the interaction between this variable and tutoring option may moderate the increase in reading comprehension, after controlling for initial score. Interaction analysis points to key elements that can explain this improvement, mainly students’ explicit use of strategies for reading comprehension, repeated episodes of reading the text aloud, and joint construction of answers. Overall, these findings support the use of peer tutoring for the development of reading comprehension throughout primary education. Limitations of the study as well as implications for research and practice are discussed.
Este estudio investiga el desarrollo de la comprensión lectora en estudiantes de primaria que participan en un programa de tutoría entre iguales. Se recogen datos de 8128 estudiantes de primaria (6–12 años) de 58 escuelas que participan en el programa entre 2012 y 2022. Se plantean dos objetivos de investigación: (1) identificar los cambios que se producen en comprensión lectora a partir de un pretest-posttest y (2) analizar la interacción de una submuestra de parejas para poder explicar los cambios detectados. Los análisis de subgrupos del pretest-posttest muestran una mejora en la comprensión lectora para todos los niveles, formatos de tutoría y roles desarrollados (.43 < ES < .97). Un modelo lineal mixto muestra que el curso y la interacción entre esta variable y la opción de tutoría pueden moderar la mejora en comprensión lectora, después de controlar el efecto de la puntuación inicial. El análisis de la interacción señala elementos clave que pueden explicar esta mejora, principalmente el uso explícito de estrategias para la comprensión lectora, la realización de lecturas repetidas en voz alta y la construcción conjunta de respuestas. En general, los resultados apoyan el uso de la tutoría entre iguales para el desarrollo de la comprensión lectora a lo largo de la educación primaria. Se discuten las limitaciones del estudio, así como las implicaciones para la investigación y la práctica.