El donante de órganos en muerte encefálica se encuentra en las Unidades de Cuidado Intensivo y los servicios de Urgencias. La participación activa de Cuidado Intensivo y del intensivista en el proceso de la donación de órganos contribuye en el aumento de las tasas de donación y de trasplante.
ObjetivoRevisar la participación de Cuidado Intensivo en la donación de órganos desde el inicio de la Red Nacional de Trasplantes en Colombia.
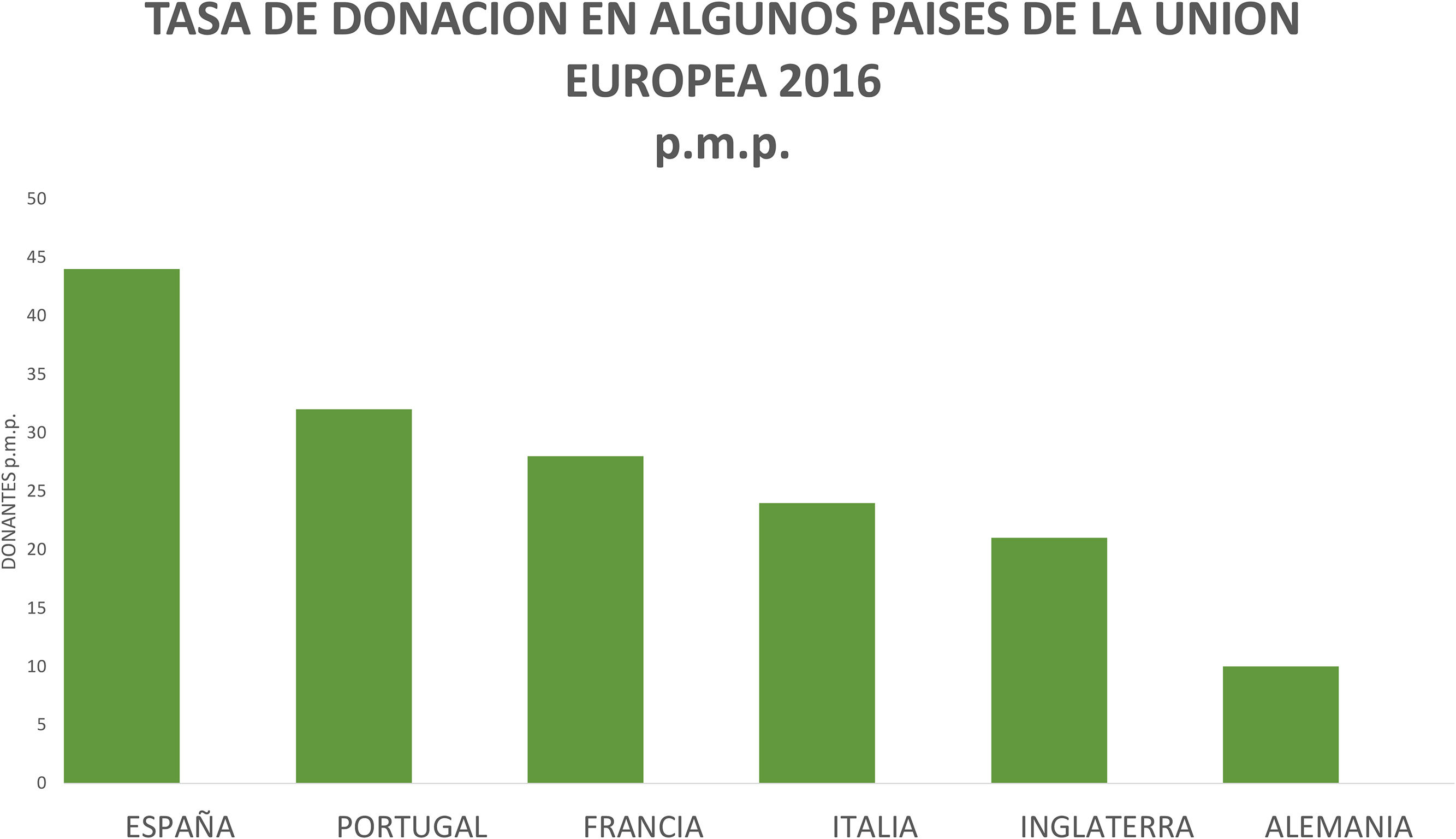
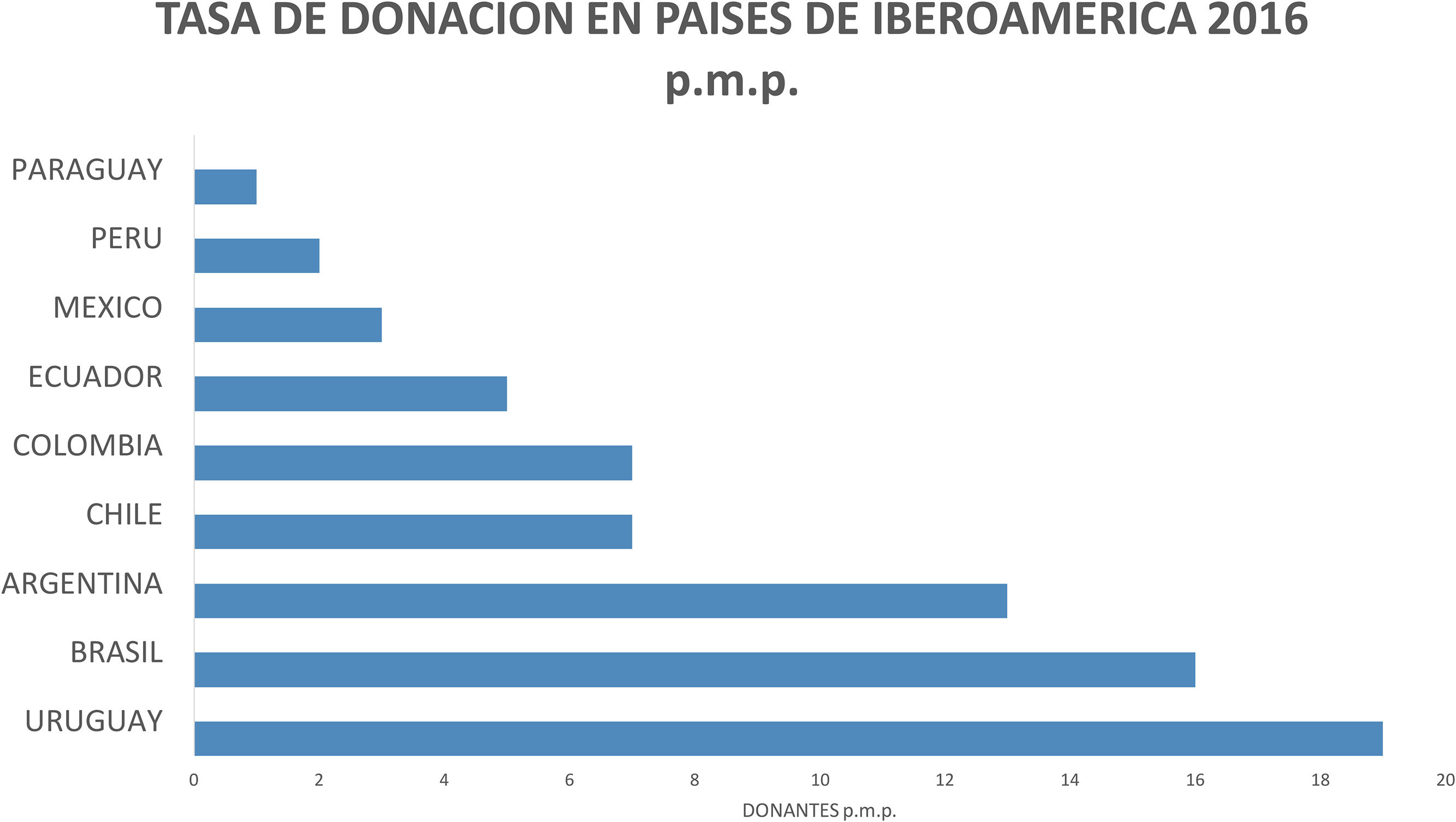
Material y métodosRevisión documental e histórica de la estructuración de la Red Nacional de trasplante liderada por el Instituto Nacional de Salud (INS) y la coordinación operativa de trasplantes. Se estableció un marco teórico sobre la participación de Cuidado Intensivo y el intensivista en la donación de órganos. Se revisaron las tasas de donación y trasplante (indicador de comparación mundial) de algunos países de Iberoamérica y Europa y Colombia, así como el comportamiento de la donación y el trasplante.
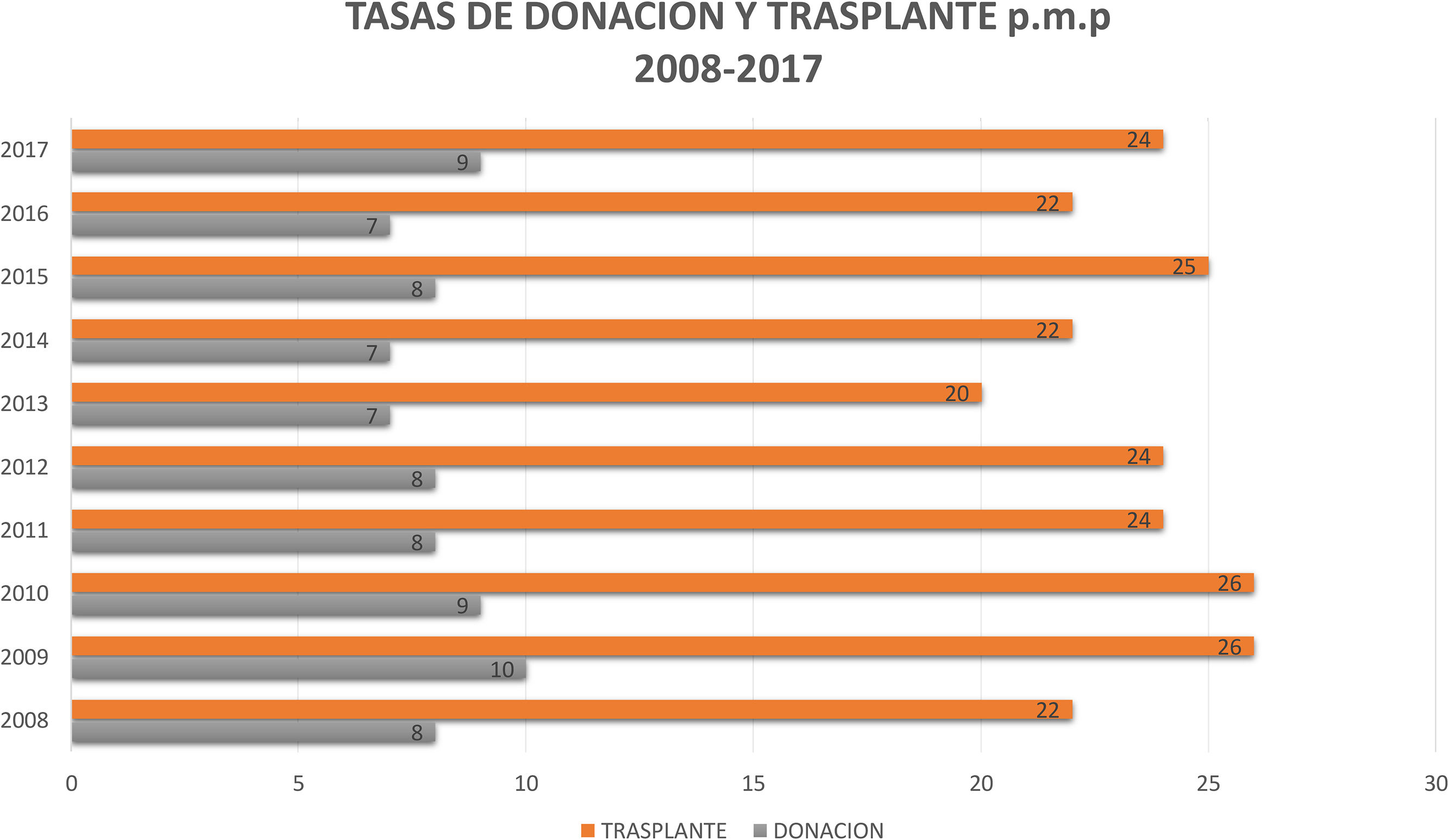
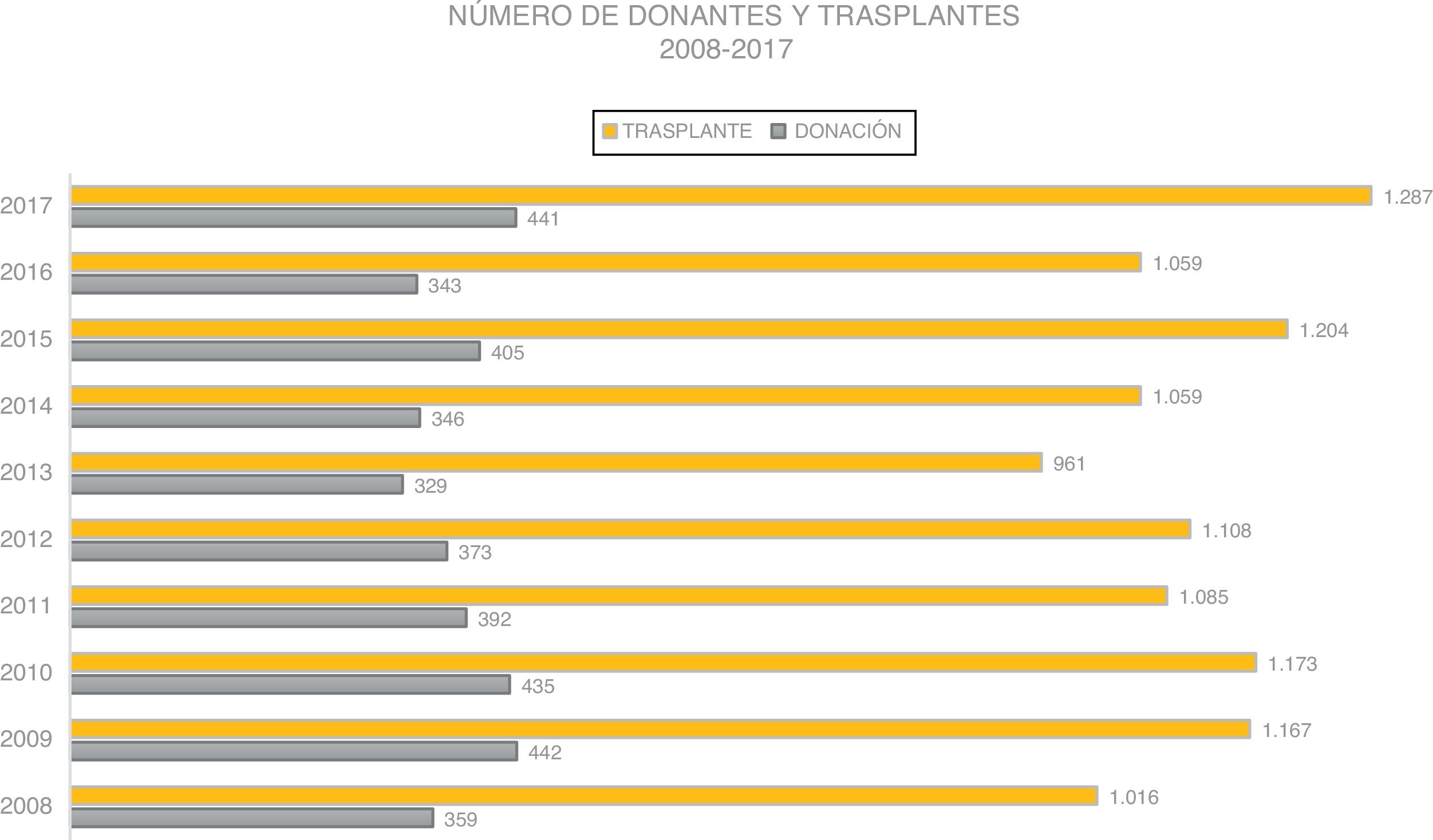
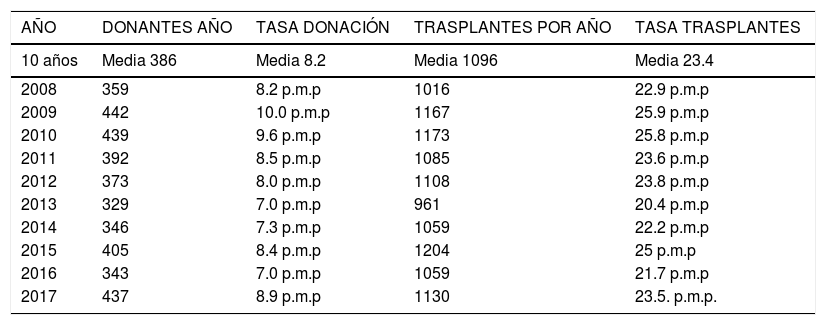
ResultadosDesde el año 2005, el INS lidera y coordina la Red Nacional de Trasplantes. La gestión operativa de la donación la realizan médicos coordinadores de trasplantes en Unidades de Cuidado Intensivo y servicios de Urgencias. La participación de Cuidado Intensivo es pasiva, nada activa, dentro del proceso de la donación. Los resultados obtenidos por la Red Nacional de Trasplantes en los últimos 10 años, con relación a la donación de órganos se mantienen constantes y no muestran variaciones importantes en el número de donantes, con media de 386 donantes reales año, rangos de 329 a 439 donantes reales por año, y tasas de donación con media de 8,2 p.m.p., rangos de 7,0 a 10 donantes p.m.p. en un país de más de 48 millones de habitantes, con un total de camas de UCI e intermedios de más 11.000 camas en 2014.
Análisis estadísticoLos valores numéricos presentados en tasas de donación y trasplante en el artículo son los aportados por la literatura médica revisada e informes del INS.
ConclusionesLa participación más activa y proactiva del talento humano de las UCI y del médico intensivista en la donación de órganos incrementará el número de donantes y las tasas de donación, aumentarán los trasplantes y las listas de espera disminuirán. Será un compromiso con el paciente, la sociedad y el trasplante.
The organ donor in brain death is in the intensive care units or emergency services. The active participation of intensive care and the Intensivist, in the process of the donation of organs, contributes in the increase of the rates of donation and of transplant.
ObjectiveTo review the participation of intensive care in organ donation since the beginning of the National Transplant Network in Colombia.
Material and methodsDocumentary and historical review of the structure of the National Transplant Network led by the National Institute of Health (INS) and the operative coordination of transplants. A theoretical framework was established on the participation of Intensive Care and the Intensivist in the donation of organs. The rates of donation and transplantation (global comparison indicator) of some countries in Latin America, Europe and Colombia were reviewed, as well as the behaviour of donation and transplantation.
ResultsSince 2005, the National Institute of Health (INS) leads and coordinates the National Transplant Network. The operative management of the donation is carried out by medical coordinators of transplants in intensive care units and emergency services. The participation of Intensive Care is not active but passive within the process of the donation. The results obtained by the National Network of Transplants in the last 10 years, in relation to the donation of organs remain constant and do not show significant variations in the number of donors, with an average of 386 real donors per year, ranges from 329 to 439 real donors per year. There was a mean donation rate of 8.2 per million population (p.m.p.) (ranging from 7.0 to 10 p.m.p.) in a country of more than 48 million inhabitants, with a total of ICU and intermediate beds of more than 11,000 in 2014.
Statistical analysisThe numerical values presented in donation and transplant rates in the article are those provided by the reviewed medical.
ConclusionsThe most active and proactive participation of the human talent of the ICUs and the Intensivist doctor in the donation of organs, will increase the number of donors, donation rates, increase the transplants and the waiting list will decrease. It will be a commitment to the patient, society and transplant.
Artículo
Socios de la Asociación de Medicina Crítica y Cuidado Intensivo
Para acceder a la revista
Es necesario que lo haga desde la zona privada de la web de la AMCI, clique aquí
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora