Mesterolone is an anabolic steroid with an acceptable indication only in very specific medical situations. However, its illicit use is growing exponentially, usually in young men who frequent gyms. It is relatively easy to skirt health regulations and acquire these often-imported compounds. Frivolous use of anabolic steroids for purposes of improving one’s bodily appearance or athletic performance may have serious health consequences of which the medical community must be aware.
Case reportA 43-year-old man, an amateur bodybuilder with no prior history of note, was admitted to our centre due to jaundice which had started one week beforehand. He did not have a rash, adenomegaly or fever. Following thorough questioning, he admitted to having used Proviron® 25 mg/12 h as a muscle enhancer for 12 days and up to three weeks beforehand.
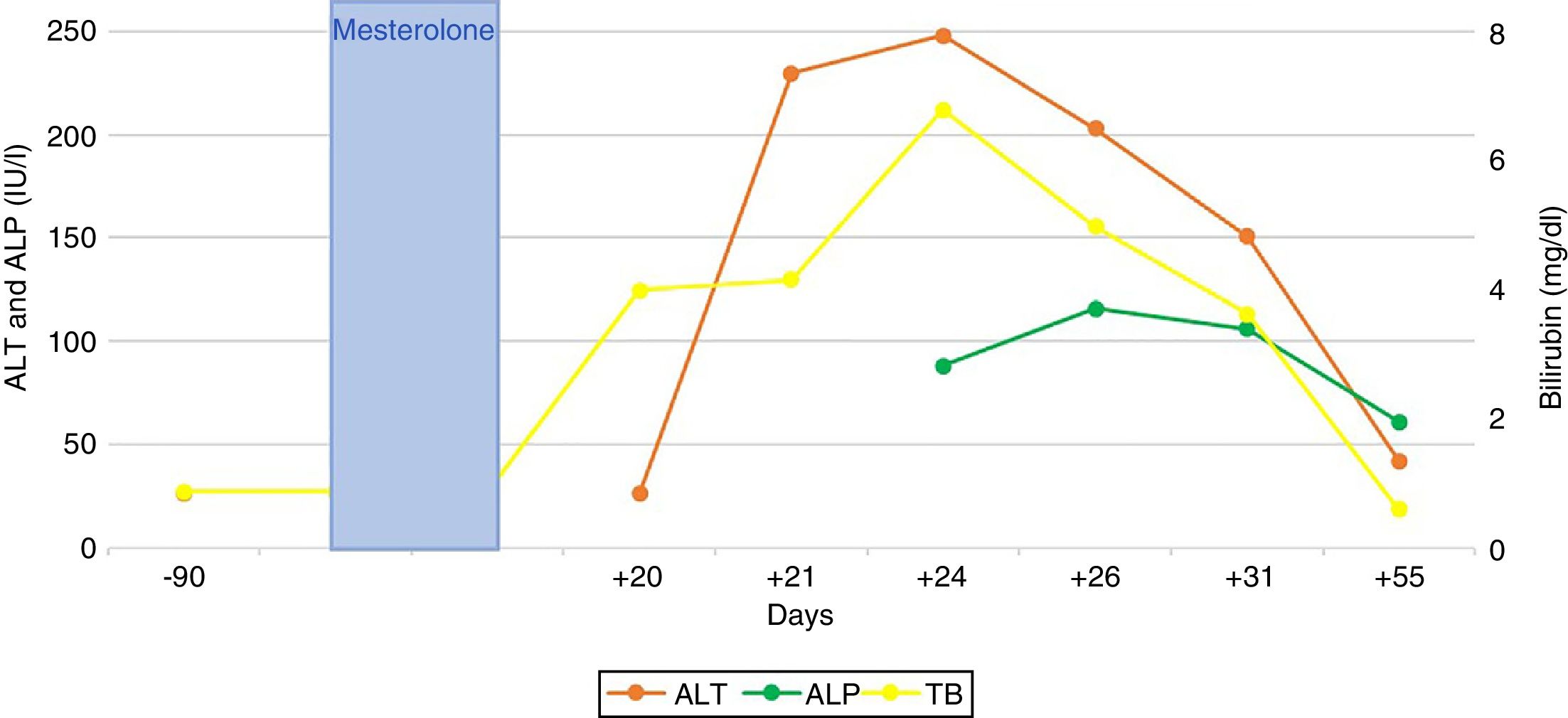
Bilirubin reached a peak level of 6.8 mg/dl; peak figures for alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and alkaline phosphatase (AP) were 248 and 116 (IU/l), respectively. The patient did not present any signs of liver failure at any time. His gammaglobulins (0.8 g/dl) and immunoglobulin G (IgG) (901 mg/dl) were normal. He had no eosinophilia (0.2 × 109/l) or lymphopenia (8.6 × 109/l). An ultrasound and magnetic resonance cholangiography intended to ascertain aetiology ruled out vascular and biliary disease. Viral causes of acute hepatitis were also ruled out (HAV-IgM, HBV-DNA, HCV-PCR, HEV-IgM, HEV-PCR, EBV-IgM and CMV-IgM were negative); liver-specific autoimmune markers were also negative.
The patient’s signs and symptoms resolved spontaneously, and his laboratory values gradually improved. He required a 12-day hospital stay and subsequent follow-up for 56 days in order to confirm full recovery for all abnormal parameters (Fig. 1).
DiscussionIn recent years, reports of cases of hepatotoxicity due to anabolic steroids have significantly increased; at present, such cases account for up to 8 % of all cases of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) in the Spanish registry of hepatotoxicity.1
The ratio between the levels of ALT and AP, both expressed in terms of multiples of the upper limit of normal (40 and 130 [IU/l], respectively), enables three classic patterns of DILI to be distinguished: cytotoxic-hepatocellular (>5), cholestatic (<2) and mixed (2–5).2 The typical pattern of hepatotoxicity of anabolic steroids is cholestatic; however, cytotoxic forms have also been reported, as in our case (6.2/0.8 = 7.7). The laboratory profiles discussed correspond, though not in full, to the type of histological lesion: up to 60 % of cases of DILI due to anabolic steroids feature histological data particular to hepatocellular lesion.3 Histological patterns of DILI due to anabolic steroids span a broad, highly varied and heterogeneous spectrum of hepatic lesions ranging from simple steatosis to liver tumours (adenomas, hepatocarcinomas and others). Peliosis hepatis has also been linked to chronic use of anabolic steroids.4
In suspicious cases, the classic CIOMS/RUCAM scale enables evaluation of causality in a simple fashion, taking into account data on temporal relationship, risk factors, course following suspension, other simultaneous drugs, concomitant aetiologies, prior information available on similar cases and, rarely, responses to re-exposure.5 In our case, a value consistent with probable hepatotoxicity (+ 8) was obtained.
As a result, there was a clear temporal association between the onset of symptoms and the use of the drug, and a secondary improvement following the suspension of the drug. In these cases, a coherent diagnosis may be made without resorting to biopsy, which is limited to situations of uncertainty and/or situations following an unfavourable course. Even in these situations of uncertainty, when diagnosis is especially complex, histological results may be non-specific.
In cases of DILI, a high level of clinical suspicion is crucial to prevent errors and delays in diagnosis, especially in patients who have acquired drugs illegally and may hide important information. The usual trend is towards spontaneous natural resolution; however, severe cases, life-threatening cases and cases resulting in death have been reported.1
Clinicians have an ethical responsibility to report cases like the one described to the health authorities. Disclosure of data from hepatotoxicity registries should raise awareness in this regard among the agents involved and promote clinical alertness to this health problem of growing magnitude.
To Dr Miren García Cortés for her wise advice.
Please cite this article as: Pérez Palacios D, Giráldez Gallego Á, Carballo Rubio V, Solà Fernández A, Pascasio Acevedo JM. Daño hepático inducido por mesterolona: a propósito de un caso. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;42:629–630.