Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) is a ubiquitous DNA virus belonging to the Herpesviridae family and causes 2 different clinical disorders: varicella and herpes zoster (HZ).1 Varicella is the primary infection caused by VZV and manifests as a highly contagious, pruriginous vesicular exanthem accompanied by fever. Varicella is more frequent in childhood, and symptoms are normally benign and self-limiting.1,2 Visceral complications, especially pneumonitis, are more frequent in adults.1,2 HZ is caused by the reactivation of latent VZV in the spinal and cranial sensory ganglia after the primary infection, and is more frequent in older or immunocompromised adults.2,3 It manifests as a painful vesicular eruption with a dermatomal distribution.2,3 Ocular manifestations (mainly conjunctivitis and keratitis) are observed when the first branch of the trigeminal nerve is involved; this condition is known as herpes zoster ophthalmicus (HZO) (up to 50% of cases).2,3
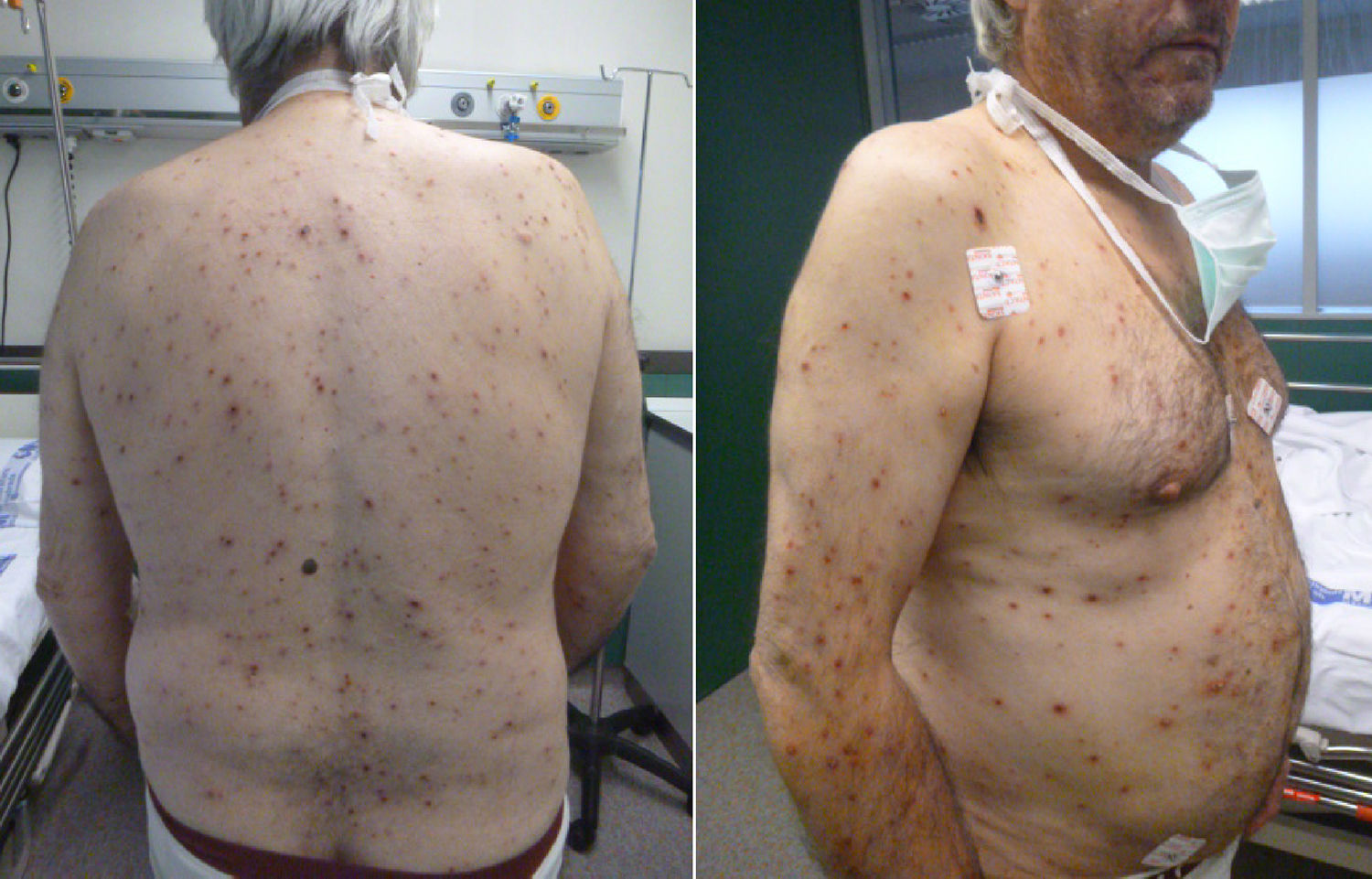
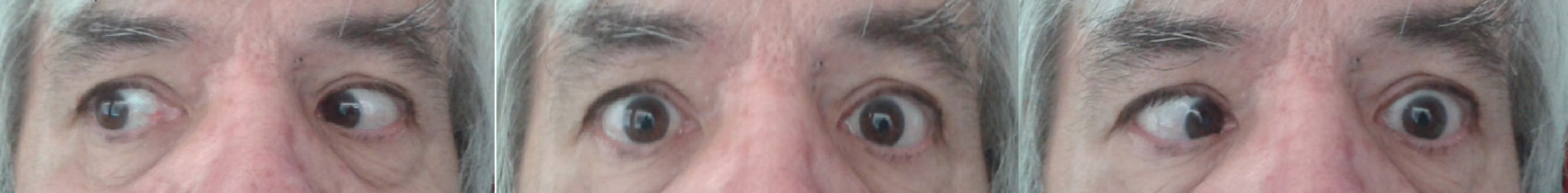
Our patient was a 59-year-old man who visited our department due to a 2-day history of diplopia. He had been diagnosed with varicella 3 days earlier due to the appearance of a vesiculopapular rash located mainly on the face and trunk, with centrifugal extension, accompanied by fever (Fig. 1). His personal history only included hypertension treated with ramipril. Three weeks previously, his 21-year-old daughter had presented varicella, which fully resolved without complication. The ophthalmological examination revealed markedly impaired adduction of the left eye (not crossing the midline) with homonymous diplopia due to incomitant strabismus when looking to the left (Fig. 2). The remaining findings were normal. No other associated neurological focal signs were observed. No relevant results were found in the following tests: erythrocyte sedimentation rate; Mantoux test; serology tests for syphilis, hepatitis B and C, and HIV; and chest radiography. Brain and orbital MRI findings were normal; a lumbar puncture revealed mononuclear pleocytosis with normal protein and glucose levels. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test was positive for VZV. The patient was diagnosed with left sixth cranial nerve palsy and meningoencephalitis secondary to VZV infection and started treatment with intravenous aciclovir dosed at 10 mg/kg/8 h for 10 days. All skin lesions resolved within one month, but diplopia persisted with no reduction in the angle of deviation at 3 months after onset. Botulinum toxin A (5 IU) was injected in the left medial rectus, inducing exotropia with hypertrophy of the left eye. No significant eye torsion or nystagmus was observed in either eye, neither did the patient display torticollis. Four months after the injection, the patient displayed orthotropic eyes with no diplopia at far or near diagnostic positions.
Several ocular manifestations have been described in association with varicella: blepharitis, scleritis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, anterior uveitis, glaucoma, acute retinal necrosis, retinal vasculitis, chorioretinitis, optic neuritis, neuroretinitis, and internal and external ophthalmoplegia.1,4 However, most of these manifestations are associated with varicella in childhood,1 since this is a very infrequent condition in adults.4 The most frequent among these complications is palpebral skin lesions associated with conjunctivitis, followed by anterior uveitis and keratitis.1 The time interval between exanthema and onset of these complications ranges from a few days to several weeks.4 Isolated paresis of cranial nerves has been described as a cause of external ophthalmoplegia secondary to VZV infection, normally in the context of HZ.3 Such other disorders as internuclear ophthalmoplegia,5 orbital apex syndrome, and orbital myositis6 are less frequently observed. Generally, known clinical characteristics of cranial nerve paresis secondary to VZV infection are caused by HZ.4 Very few cases have been reported of cranial nerve palsy as a complication of varicella (with cases of seventh, sixth, and third cranial nerve involvement, in order of frequency)7; anecdotal cases of orbital myositis are also reported. In this case, extraocular muscle paresis appeared several days after the rash, which may be due to a direct cytopathic effect of the virus.3,8 The presence of lymphocytes in the intrathecal space and the positive PCR findings suggest VZV infection of the central nervous system. In other reported cases, more delayed onset (weeks after exanthema) and/or intrathecal production of IgG and IgM immunoglobulins suggest immune pathogenesis or occlusive vasculitis induced by VZV.
Treatment consists of the administration of antiviral agents capable of crossing the blood-brain barrier (aciclovir, valaciclovir, or famciclovir).2,3 Concomitant treatment with corticosteroids may also be beneficial in ophthalmoparesis. Prognosis of ophthalmoparesis in HZ is favourable (recovery at one year in 87.5% of cases).3 In the few reported cases associated with varicella (in children), clinical course seems not to be worse.8
In this case, paresis persisted and treatment with botulinum toxin was curative despite initial complications. In conclusion, varicella in adulthood may be complicated by sixth cranial nerve palsy. Prognosis was favourable after antiviral treatment and botulinum toxin injection.
Please cite this article as: Reche-Sainz JA, et al. Parálisis de sexto nervio craneal en adulto inmunocompetente con varicela. Neurología. 2020;35:220–221.