La hipotermia perioperatoria se asocia a efectos adversos que aumentan la morbilidad y la mortalidad. El objetivo de este estudio fue identificar los factores de riesgo para hipotermia intraoperatoria y construir una herramienta para identificar a los pacientes de alto riesgo.
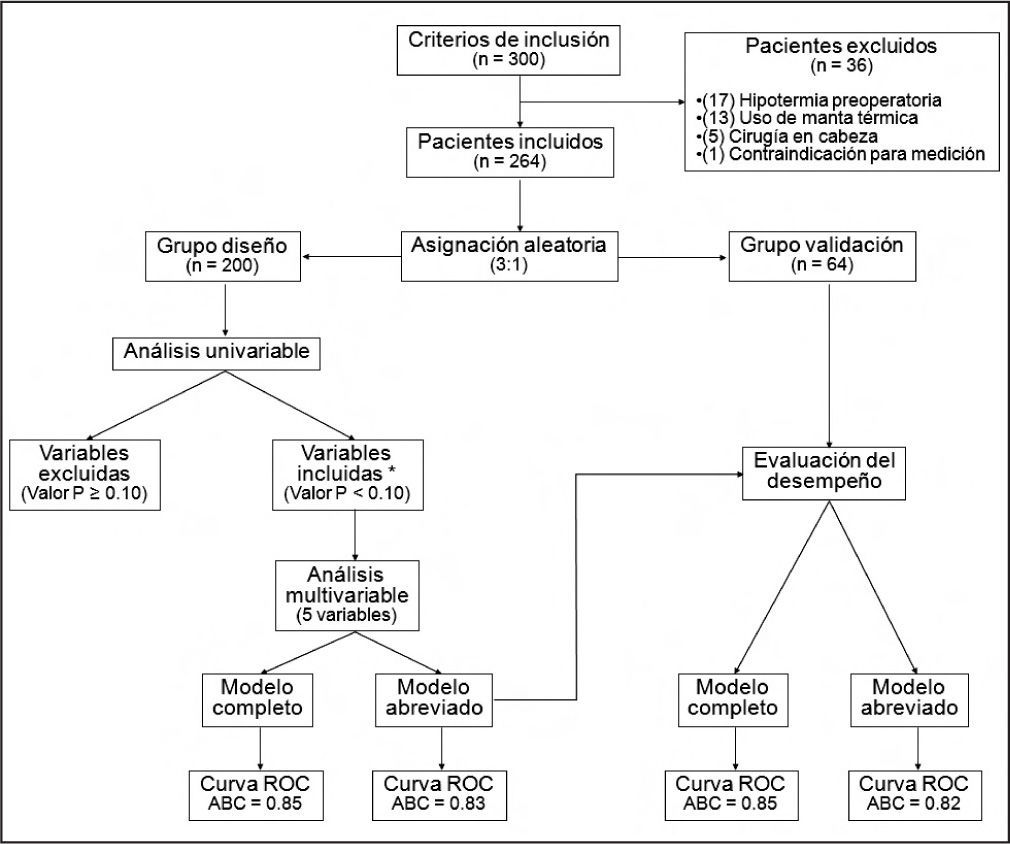
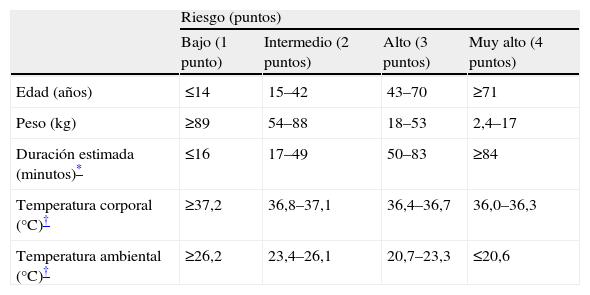
Material y métodos:Se estudiaron pacientes, sin límite de edad, en los que se realizó algún procedimiento quirúrgico. Fueron asignados a dos grupos “diseño” y “validación” mediante una lista de números generados al azar. La hipotermia intraoperatoria se definió como una temperatura timpánica de 35,9°C o menos. En un análisis bivariable en el grupo diseño se identificaron los factores predictores y después en un modelo multivariable (regresión logística de eliminación progresiva de variables no significativas) se obtuvo un modelo predictivo. Además, se elaboró una tabla de puntuación transformando las variables (modelo abreviado). El poder predictivo se determinó mediante el área bajo la curva ROC [área bajo curva ROC (ABC-ROC)].
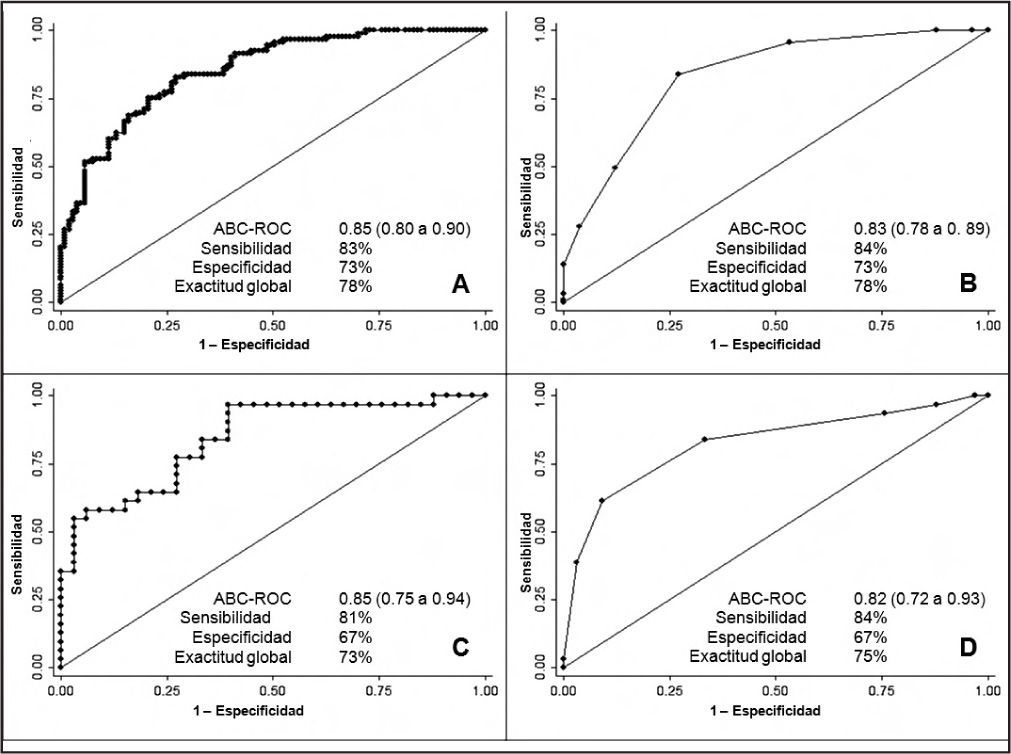
ResultadosSe incluyeron 264 pacientes consecutivos; 200 en el grupo diseño y 64 en el de validación En el grupo diseño el ABC-ROC del modelo completo fue 0,85 y la del modelo abreviado ABC-ROC 0,83. En el grupo validación el ABC-ROC del modelo competo fue 0,85 y la del modelo abreviado ABC-ROC 0,82. El valor P fue < 0,01 en todas las curvas.
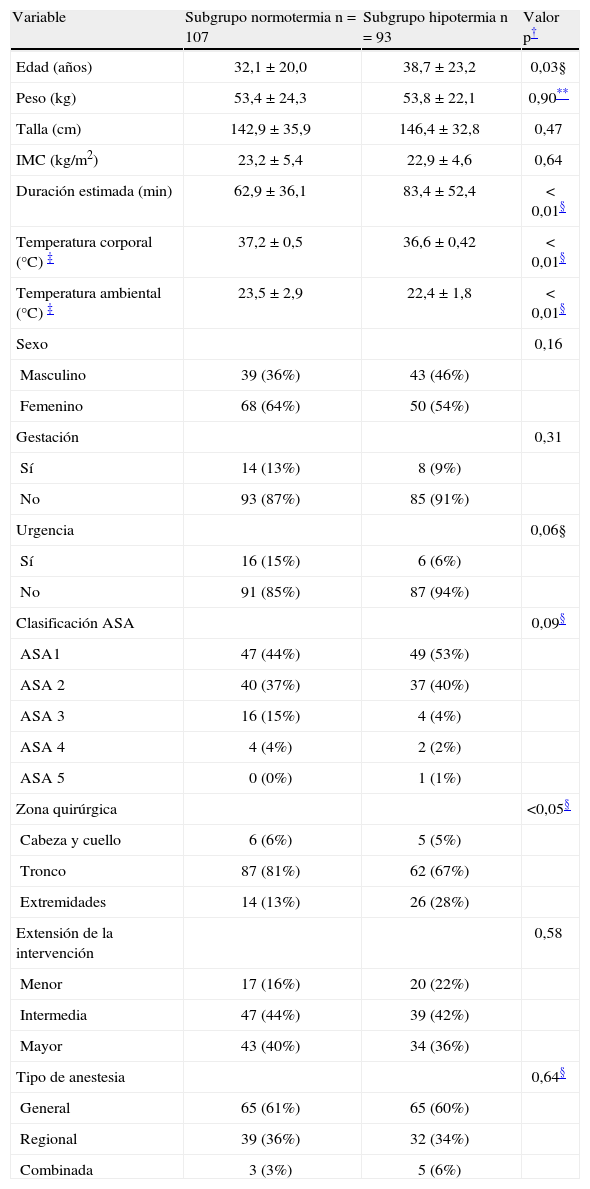
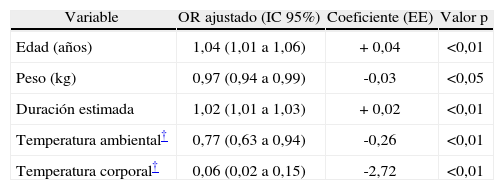
ConclusiónEn nuestro estudio, la edad, peso, duración estimada del procedimiento y las temperaturas corporal y ambiental durante la inducción, incluidas en un modelo predictivo, fueron factores preoperatorios que predicen el desarrollo de hipotermia intraoperatoria en una muestra heterogénea de pacientes quirúrgicos.
Perioperative hypothermia is linked to adverse effects that increase morbidity and mortality. The objectives of this study were to identify the risk factors for intraoperative hypothermia and construct an instrument for identifying patients at high risk.
Materials and methodsWe studied patients of all ages who had undergone surgery. Patients were assigned to a design group or a validation group by means of a list of randomly generated numbers. Intraoperative hypothermia was defined by an tympanic temperature of 35.9°C or less. A bivariate analysis of the design group identified the predictive factors and a multivariate analysis (logistic regression with backward elimination of nonsignificant variables) provided a predictive model. Risk scores were obtained for each variable by converting them to a 4-degree risk scale (abbreviated model). Predictive power was determined by calculating the area under the receiver-operator characteristic curve (AUC).
ResultsWe enrolled 264 consecutive patients; 200 were assigned to the design group and 64 to the validation group. In the design group, the AUC was 0.85 for the complete model and 0.83 for the abbreviated model. In the validation group, the AUC was 0.85 for the complete model and 0.82 for the abbreviated model. The P value was <.01 for all curves.
ConclusionAge, weight, approximate duration of surgery, and body and ambient temperature during induction were the included factors that predicted intraoperative hypothermia in a heterogeneous sample of surgical patients.