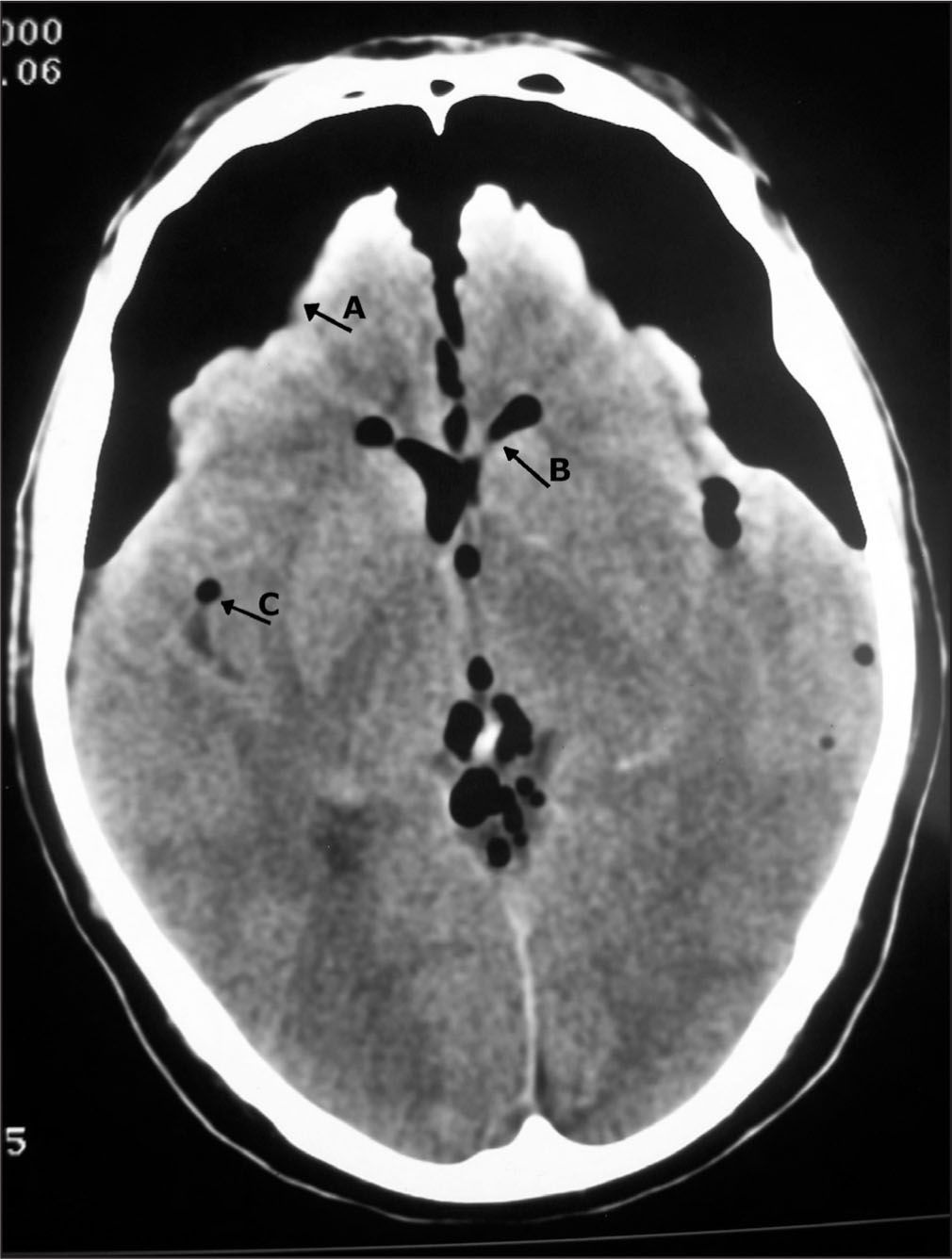
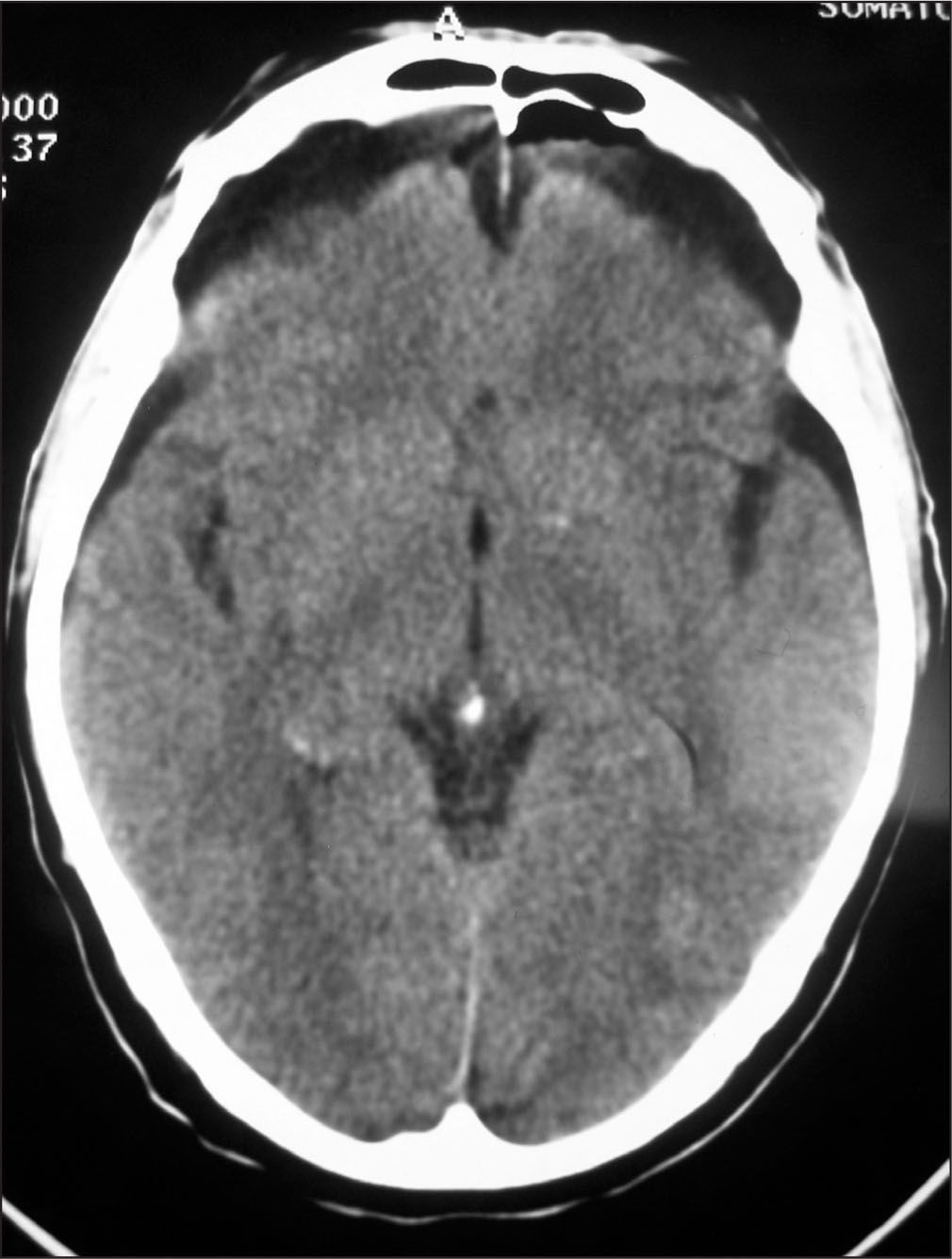
Presentamos el caso de un varón de 70 años, ASA II que desarrolló un neumoencéfalo masivo secundario a una fístula entre los espacios subaracnoideo y pleural tras una neumonectomía izquierda. Tras un postoperatorio inmediato sin incidencias, el paciente reingresó en la unidad de reanimación por disnea, cefalea intensa, confusión y disminución del nivel de conciencia. La tomografía computarizada confirmó la presencia de una fístula de líquido cefalorraquídeo secundaria a apertura del espacio intradural durante la resección tumoral. Se optó por un tratamiento conservador consistente en reposo en posición de ligero Trendelemburg, profilaxis antibiótica para prevenir una meningitis, manteniendo el tubo de drenaje torácico con sello de agua.
We report the case of a 70-year-old man (ASA physical status 2) who developed massive pneumocephalus caused by a fistula between the subarachnoid and pleural spaces following a left pneumonectomy. After an uneventful immediate postoperative period, the patient was readmitted to the recovery care unit with dyspnea, intense headache, confusion, and diminished level of consciousness. Computed tomography confirmed a cerebrospinal fluid fistula secondary to the opening of the intradural space during tumor resection. Treatment was conservative, consisting of rest in a slightly Trendelenburg position, antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent meningitis, and a water seal on the thoracic drainage tube.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora