Analizar la aplicación del score predictivo (SP) de Cameron para la traqueostomía reglada (TR) en cirugía tumoral oral.
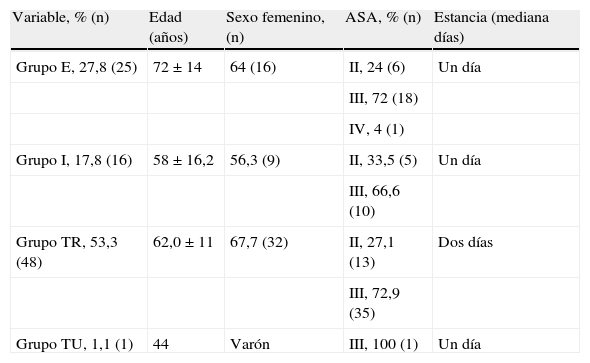
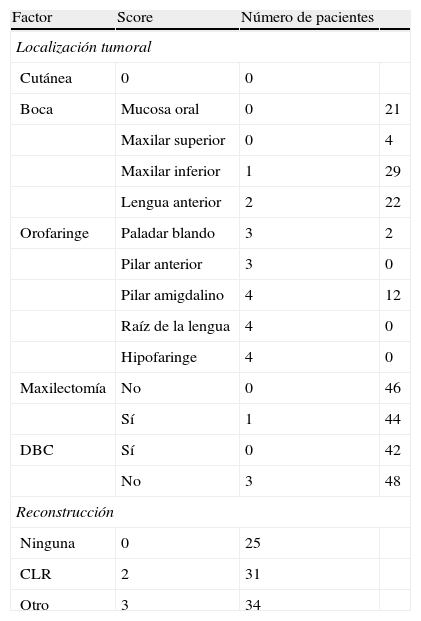
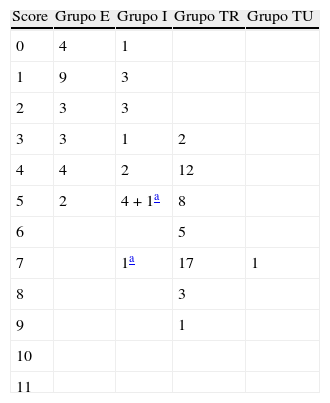
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo y descriptivo de pacientes intervenidos de cirugía tumoral oral consecutivamente entre enero de 2010 y diciembre de 2012. Se recogieron los ítems del SP: la reconstrucción y el tipo de injerto, la maxilectomía inferior, la disección bilateral cervical y la localización tumoral. Se agruparon los pacientes según el manejo de la vía aérea al final de la cirugía en 4 grupos: extubados, intubados, TR y traqueostomía urgente. Se consideró un punto de corte≥5 puntos del SP para la realización de TR.
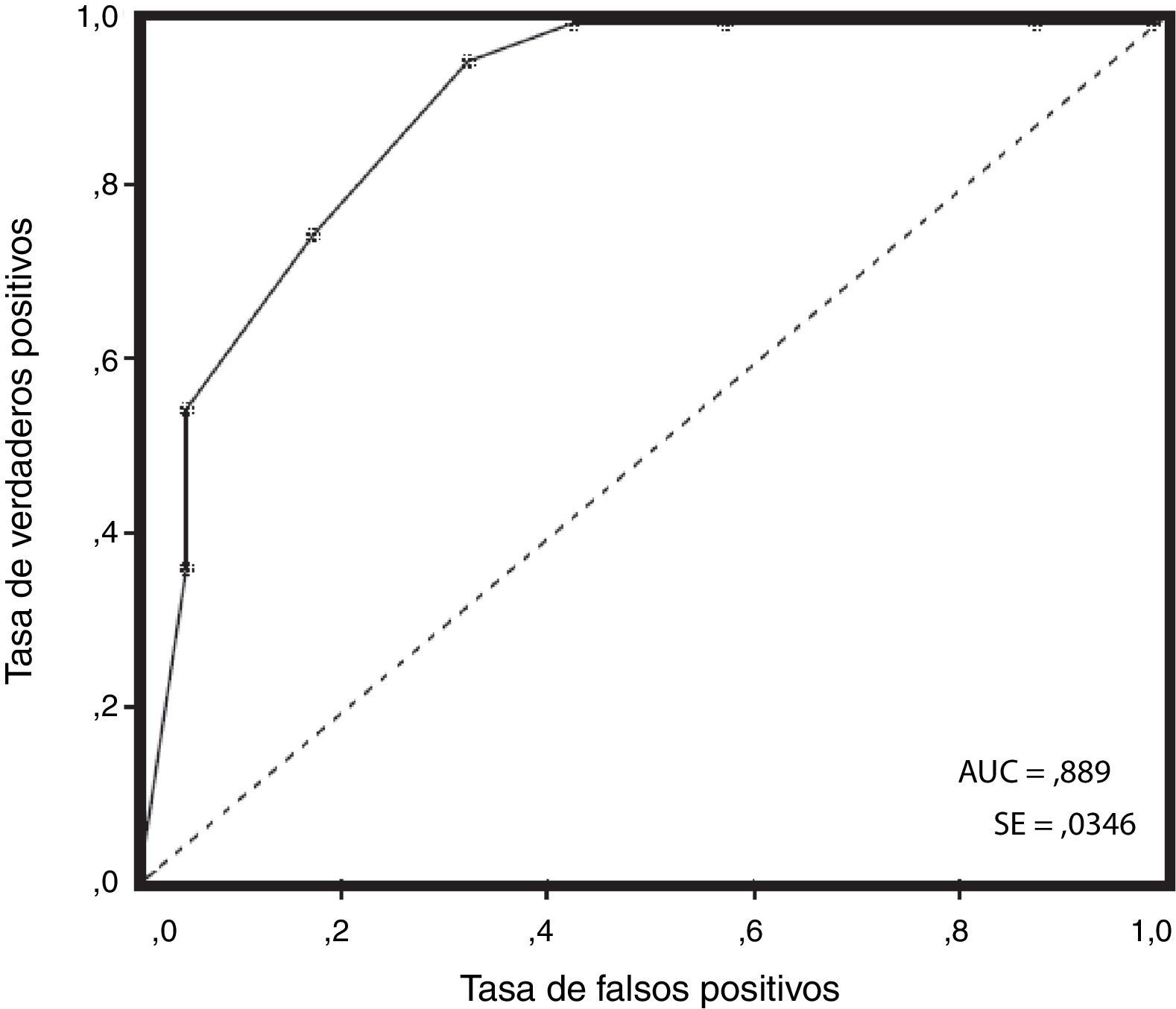
ResultadosSe registraron un total de 90 pacientes. La distribución por grupos fue: extubados=27,8% de los casos, intubados=17,8%, TR=53,3% y un caso (1,1%) de traqueostomía urgente. Los 3 pacientes en los que se efectuó una traqueostomía no reglada tenían un SP≥5 puntos. Usando el valor del SP≥5 puntos se obtuvo un valor de sensibilidad diagnóstica de 0,7 para un intervalo de confianza (IC) del 95% de 0,57-0,82 y un valor de especificidad diagnóstica de 0,9 (IC del 95% 0,79-0,99). El VPP fue de 0,9 (IC del 95% 0,81-0,99) y el VPN de 0,67 (IC del 95% 0,54-0,8). El ABC dio un valor de 0,87 (error estándar 0,36). El cociente de probabilidad positivo fue 6,48.
ConclusiónLa decisión de realizar una TR durante la cirugía tumoral oral puede reforzarse utilizando el SP de Cameron basándose en datos objetivos.
The aim of this study was to analyze the results of applying the predictive score (PS) of Cameron to perform elective tracheostomy (ET) in oral tumor surgery.
Material and methodsA retrospective and descriptive study was conducted on consecutive patients undergoing oral tumor surgery between January 2010 and December 2012. Items of the PS were collected: reconstruction and type of graft, mandibulectomy, bilateral neck dissection, and tumor location. Patients were grouped according to the management of the airway at the end of surgery into 4 groups: extubated, intubated, ET, and urgent tracheostomy. A cutoff of≥5 points PS was considered for conducting ET.
ResultsA total of 90 patients were included. Group distribution was: extubated=27.8%, intubated=17.8%, ET=53.3%, and one case (1.1%) of urgent tracheostomy. Using the cutoff value of PS≥5 points yielded a diagnostic sensitivity value of 0.7 for a 95% confidence interval (CI) (0.57 to 0.82), and a diagnostic specificity value of 0.9 (95% CI 0.79 to 0.99). The PPV was 0.9 (95% CI 0.81 to 0.99) and the NPV was 0.67 (95% CI 0.54 to 0.8). The AUC gave a value of 0.87 (standard error 0.36). The likelihood ratio was 6.48.
ConclusionThe decision to perform an ET for oral tumor surgery can be enhanced using the PS of Cameron based on objective data.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora