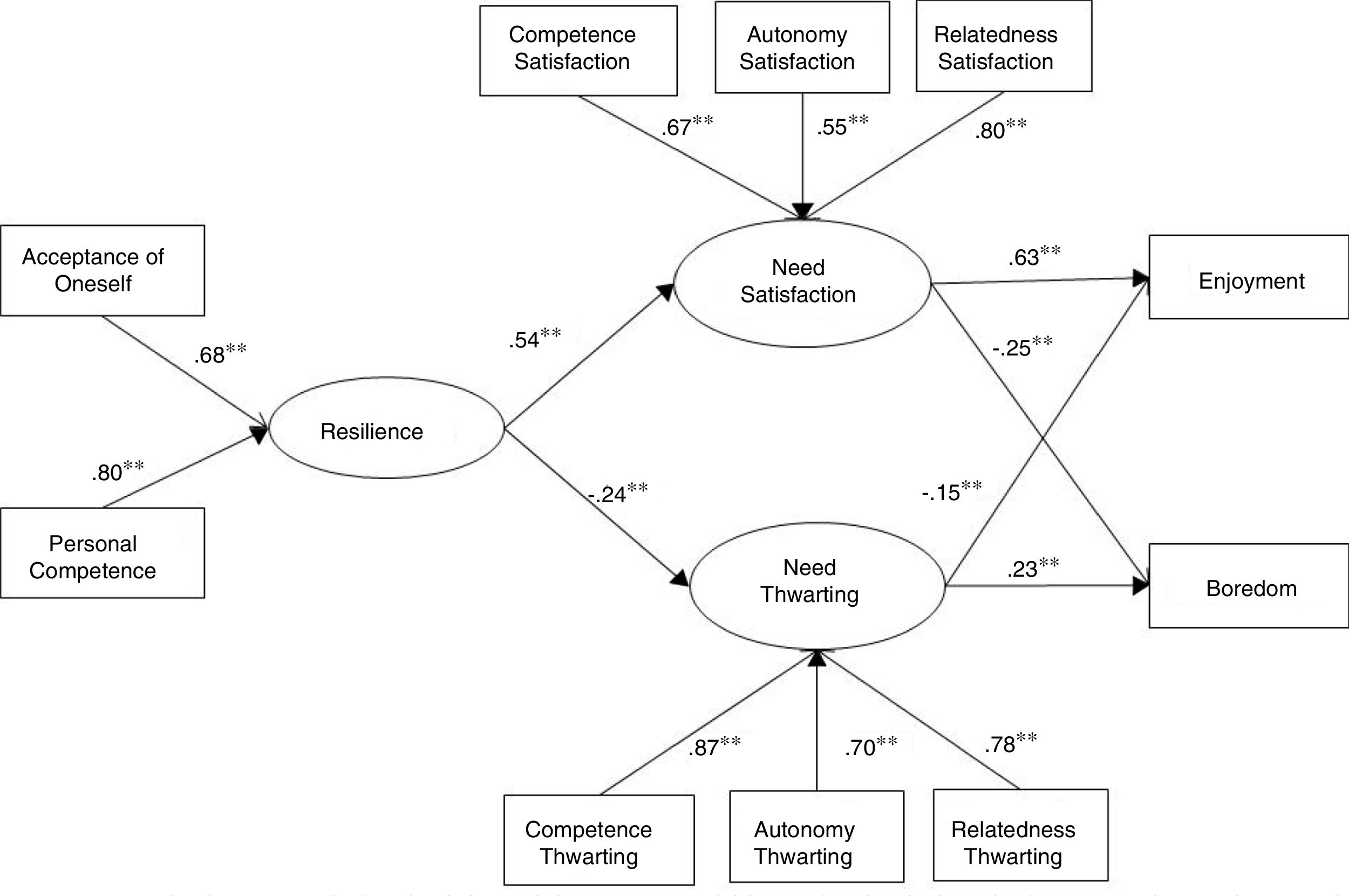
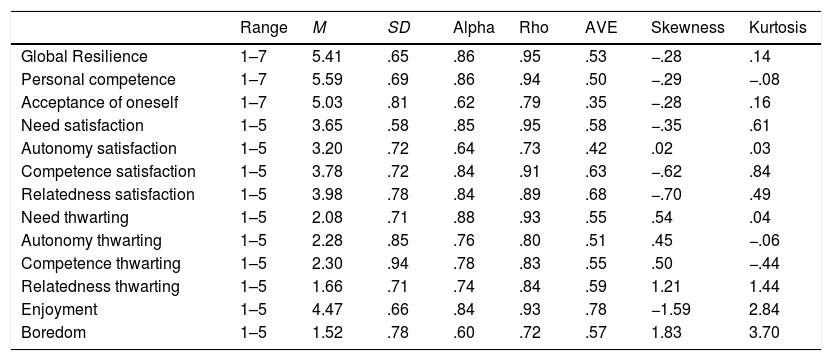
Positive psychology defends that resilience and satisfaction of the basic psychological needs contribute to predict athletes’ quality of engagement and optimal development. Based on self-determination theory the present study aims to test a model analyzing the relationship between young athletes’ resilience, satisfaction and thwarting of their basic psychological needs, and their experiences of enjoyment and boredom within their sport practice. Participants of the study are 641 female football and basketball players (Mage=14.74±3.91). Results of the structural equation models show that athletes’ resilience is positively associated with satisfaction of basic psychological needs and negatively with its thwarting. Players’ psychological needs satisfaction is positively associated with their enjoyment and negatively with their boredom, whereas needs thwarting is positively associated with their boredom and negatively with their experience of enjoyment. Finally, the results show the total mediation of the satisfaction and thwarting of the psychological needs in the relationship between resilience and experiences of enjoyment and boredom. These results emphasize the importance of developing athletes’ resilience as it promotes satisfaction and prevents thwarting of the basic psychological needs fostering quality of sport engagement.
La psicología positiva defiende que las variables que promueven la calidad de la implicación, como la resiliencia y la satisfacción de las necesidades psicológicas básicas, contribuyen a predecir el desarrollo óptimo. Desde el marco de la teoría de la autodeterminación, en el presente estudio se analiza la relación entre la resiliencia, la satisfacción y la frustración de las necesidades psicológicas básicas y las experiencias de diversión y aburrimiento en la práctica deportiva. En el estudio participan 641 jugadoras de fútbol y baloncesto (Medad=14.74±3.91). Los resultados del análisis de ecuaciones estructurales muestran que la resiliencia se asocia positivamente con la satisfacción y negativamente con la frustración de las necesidades psicológicas de las deportistas. La satisfacción de las necesidades psicológicas se asocia positivamente con la diversión y negativamente con el aburrimiento, mientras que la frustración se asocia positivamente con el aburrimiento y negativamente con la diversión. Por último, los resultados muestran la mediación total de la satisfacción y frustración de las necesidades psicológicas en la relación entre la resiliencia y las experiencias de diversión y aburrimiento. Estos resultados enfatizan la importancia de promover la resiliencia de las jugadoras ya que con ello se fomenta la satisfacción y se dificulta la frustración de sus necesidades psicológicas básicas, promoviendo la calidad de la implicación deportiva.