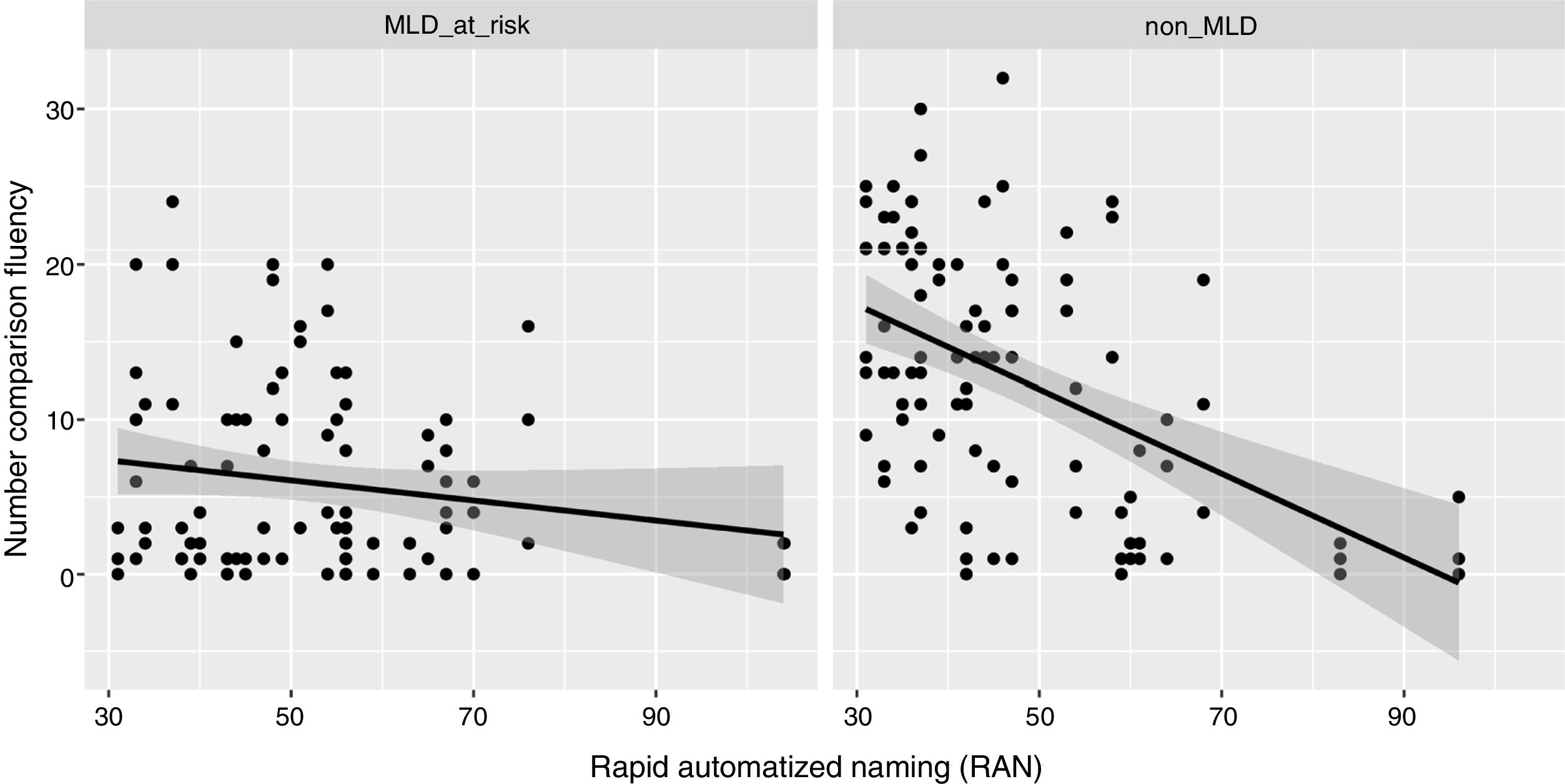
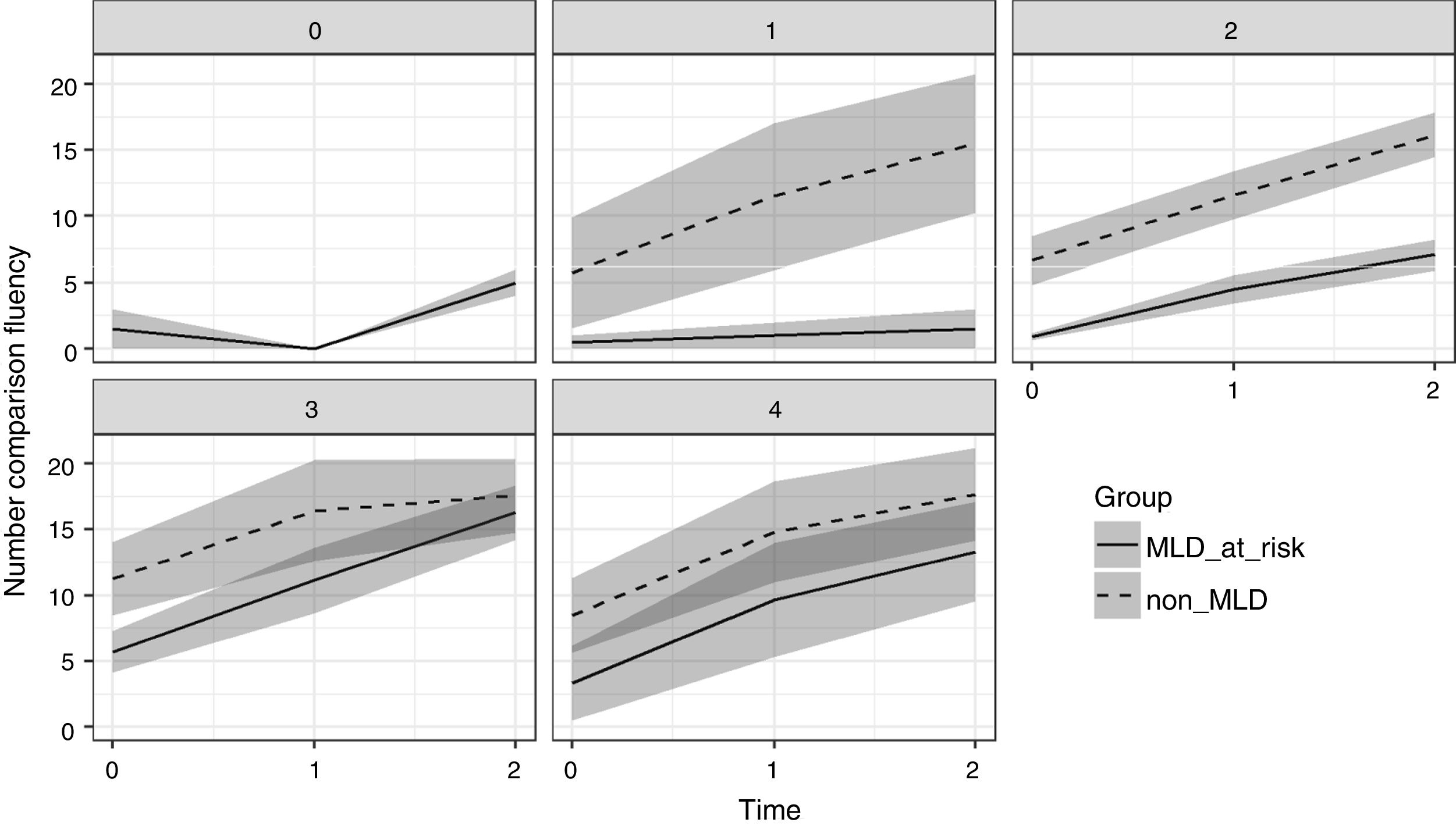
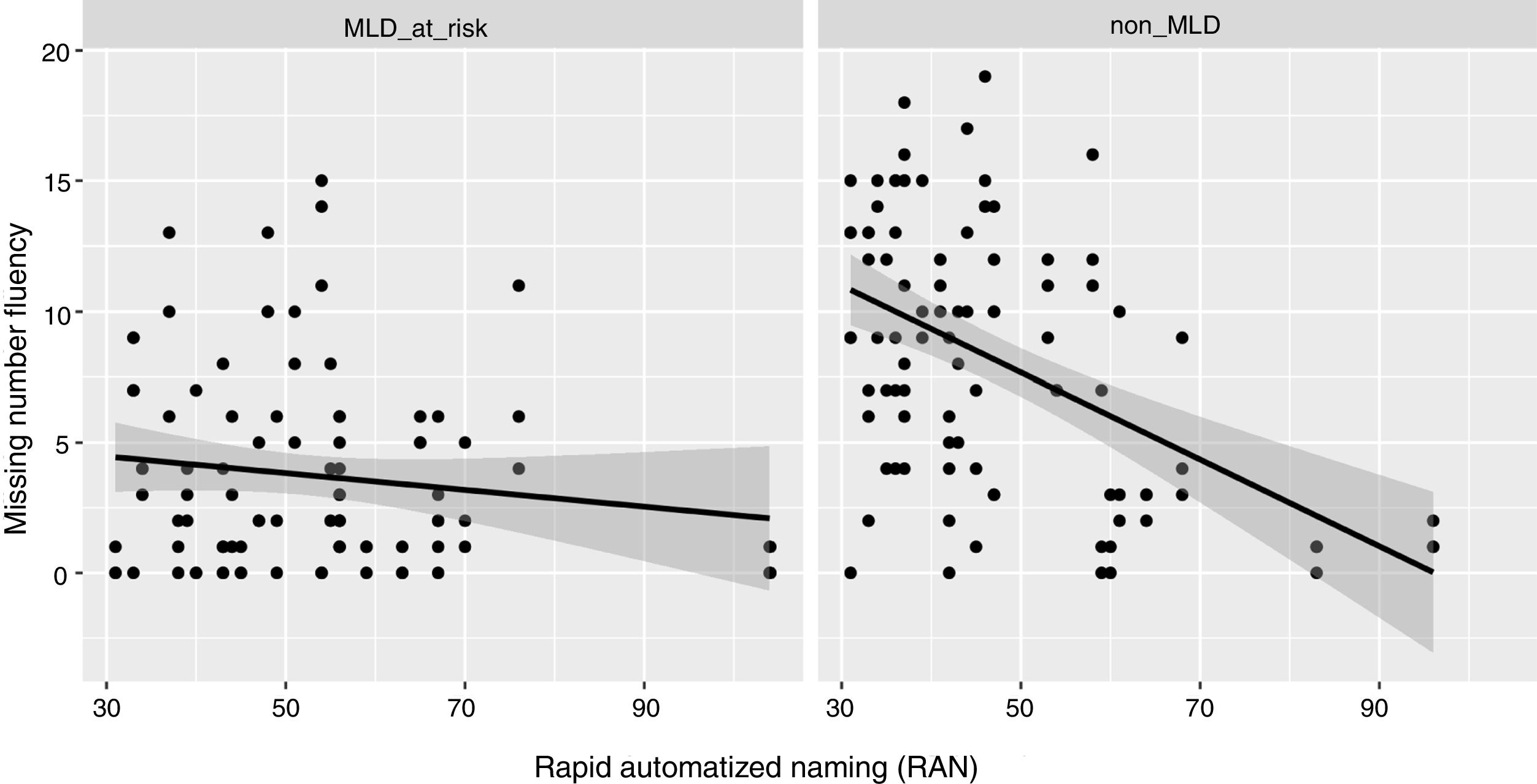
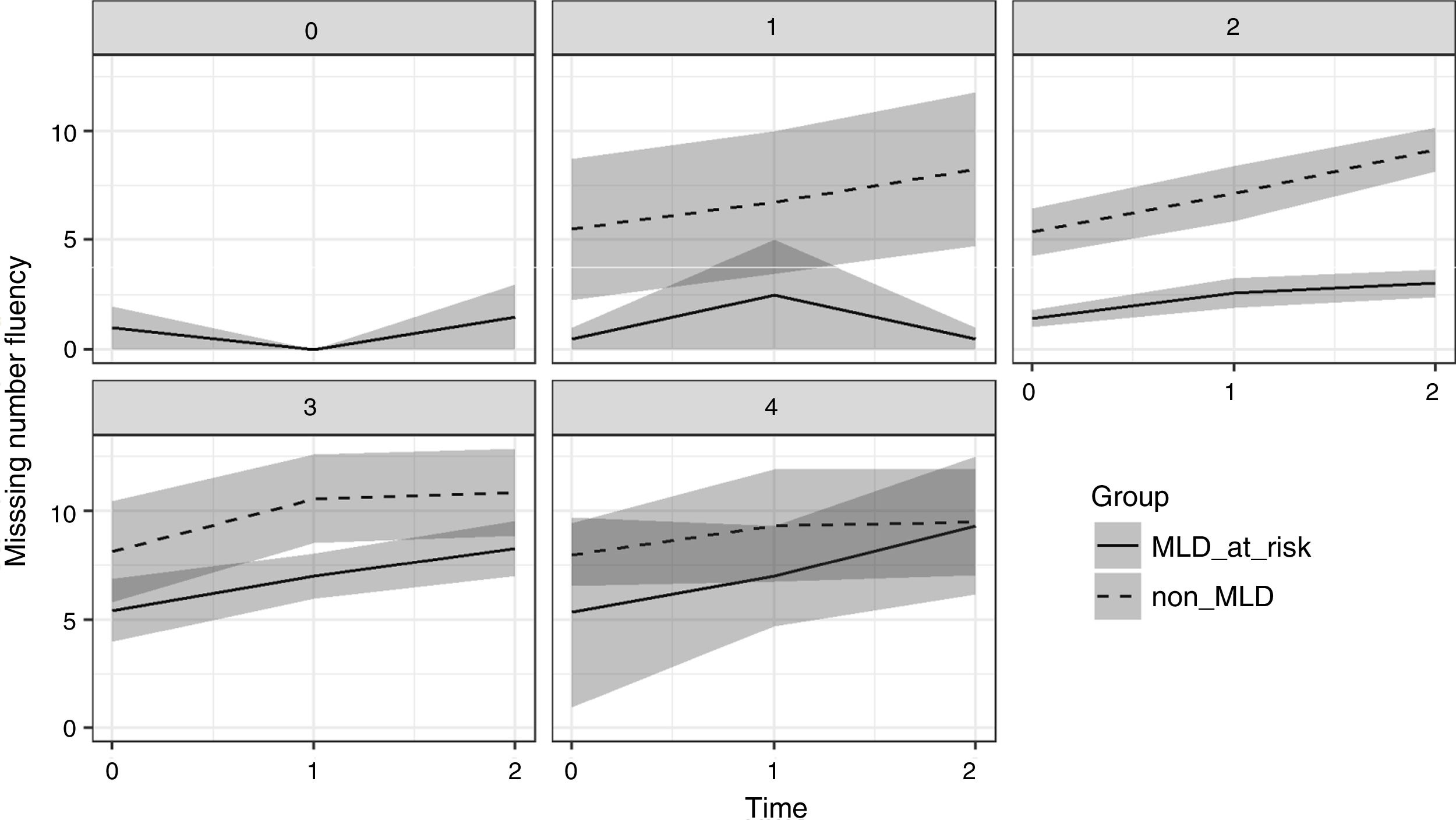
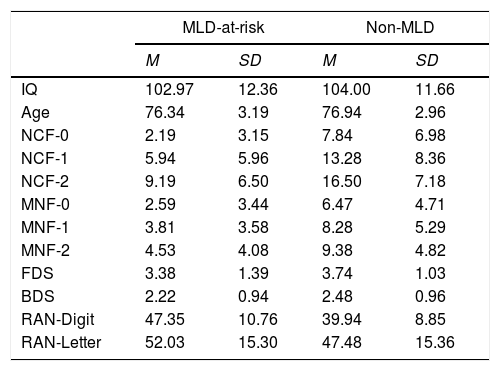
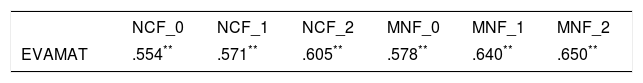
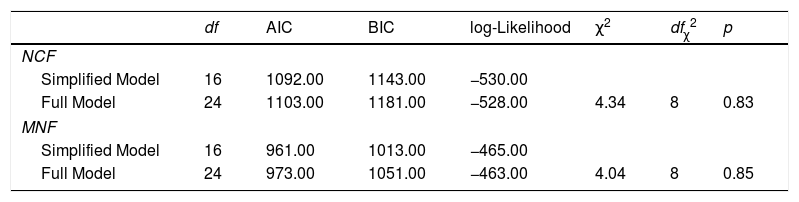
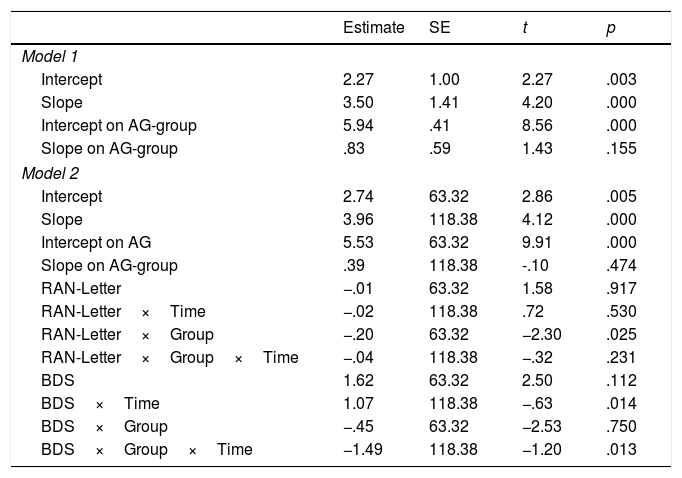
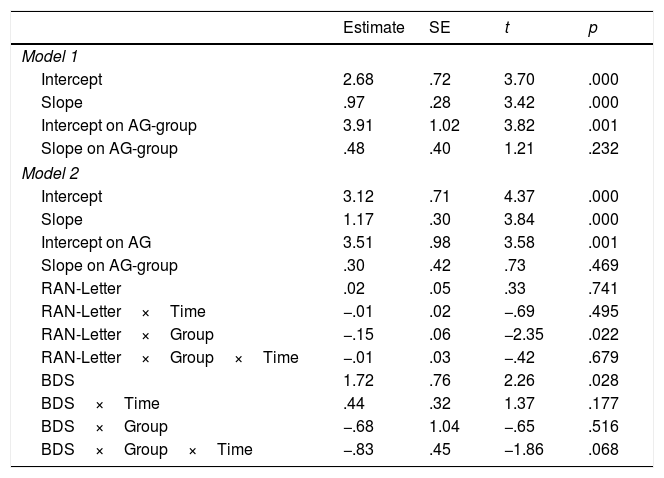
The present study examined the contribution of working memory and Rapid Automatized Naming (RAN) to growth trajectories in number processing, measured using Curriculum-based Measurement (CBM). Participants were two groups of first grade children; one group were at risk of developing mathematics disabilities (MLD-at-risk, n=32), and the other included typically developing (non-MLD, n=32) children. Of all the cognitive measures, backward digit span (BDS) tasks and RAN-Letter made significant contributions to differentiating group performance. RAN-Letter provided differentiation of groups, and BDS provided differentiation of the growth rates of both groups in number processing skills. These results highlight the relevance of RAN and BDS for the development of number processing skills in first grade, especially for MLD-at-risk children. BDS is therefore a very important task to be measured during the early stages of mathematics instruction, because it predicts deficits in development of number skills.
En el presente estudio se investiga el efecto de la memoria de trabajo y la denominación automatizada rápida (RAN) en las trayectorias de crecimiento del procesamiento numérico, medido mediante Medidas Basadas en el Curriculum (CBM). Se evaluan dos grupos de niños de primer grado; un grupo en riesgo de desarrollar dificultades específicas de aprendizaje en matemáticas (MLD-en riesgo, n=32), y otro compuesto por niños con desarrollo típico (sin-MLD, n=32). De todas las medidas cognitivas administradas, se evidencia que la tarea de span verbal de dígitos inversos (BDS) y la subtarea de RAN-Letras contribuyen significativamente en la diferenciación del rendimiento de los grupos. RAN-Letras contribuye a la diferenciación de los grupos en el rendimiento de habilidades numéricas, mientras BDS contribuye de forma diferenciada a la ratio de crecimiento de los grupos en habilidades numéricas. Estos resultados visibilizan la relevancia de RAN y BDS para el desarrollo de habilidades de procesamiento numérico en primer grado, especialmente para niños en riesgo de MLD. Así, BDS emerge como una tarea importante a evaluar durante las primeras etapas de la instrucción matemática, debido su capacidad de predecir déficits en el desarrollo de habilidades numéricas.