To evaluate plans using volumetric modulated arc therapy techniques specifically for synchronous bilateral breast cancer patients undergoing right-sided lumpectomy, left-sided mastectomy and regional lymph node dissection (level I & II axillary lymph nodes).
MethodsEleven bilateral breast cancer patients underwent right-side lumpectomy, left-sided mastectomy, and regional lymph node dissection. The patients underwent CT simulation and 3D contouring had been done by Focalsim soft wear from Elekta and Monaco 5.1 treatment planning system by Elekta was used for planning, then the treated with either 6 or 10 MV photon beam energy using a Synergy lineal accelerator.
ResultsVMAT provided sufficient dose coverage and a high dose conformity index for all right breast, left chest wall and lymph node (level III axilla & IX lymph node) targets. The dose distribution was almost homogenous. The correlation between the monitor units and the conformity indices was significant for both the right and the left breast but not significant for the regional nodal volume target. There was no significant correlation between the monitor units and homogeneity indices for right or left targets, but there was a significant correlation for the nodal volumes.
ConclusionVMAT is an effective treatment technique for bilateral breast cancer patients, providing a highly conformal dose and a good dose distribution. The correlation between the MU and the dose conformity serves as a useful evaluation tool for this technique.
Evaluar una estrategia de tratamiento para pacientes con cáncer de mama bilateral sincrónico sometidas a tumorectomía del lado derecho, mastectomía del lado izquierdo y linfadenectomía.
MétodosOnce pacientes con cáncer de mama bilateral se sometieron a tumorectomía del lado derecho, mastectomía del lado izquierdo y linfadenectomía de los niveles I y II axilares. La delimitación de volúmenes se realizó mediante Focalsim, la planificación se realizó con Monaco 5.1 de Elekta y se trataron con energía de haz de fotones de 6 o 10 MV utilizando un acelerador lineal Synergy.
ResultadosVMAT proporcionó una cobertura de dosis suficiente y un alto índice de conformidad para todos los volúmenes de mama izquierda, mama derecha y ganglios linfáticos. La distribución de dosis fue casi homogénea. La correlación entre las unidades de monitor y los índices de conformidad fue significativa para ambas mamas, pero no llegó a la significación en volumen supraclavicular. No hubo una correlación significativa entre las unidades de monitor y los índices de homogeneidad para ambas mamas, pero hubo una correlación significativa para los ganglios linfáticos.
ConclusiónVMAT es una técnica de tratamiento eficaz para pacientes con cáncer de mama bilateral, que proporciona una cobertura de dosis suficiente con un alto índice de conformidad. La correlación entre el número de unidades de monitor y el índice de conformidad sirve como una herramienta de evaluación útil para esta técnica.
Treatment planning during the radiation therapy course for the patient is challenging and depends on the technique used and the experience of the medical physicist. In the 1990s, the three-dimensional technique dominated. At the end of the 1990s, a new technique was proposed by Yu1,2 to reduce the treatment time for patients during irradiation with a high dose distribution.3,4 The basic idea of this technique is to use different arcs of the gantry and multileaf collimators to build high modulation fluences. In 2003, Crooks et al. developed this technique by changing the possibilities of intensity-modulated arc therapy (IMAT), which has given rise to several planning algorithms using a single gantry arc with multiple vigorous leaf motions.5 Modern lineal accelerators are equipped with accessories that vary the gantry speed, dose rate, multileaf collimator (MLC) leaves and angle simultaneously. This technique is known as volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT).6,7 Bilateral breast cancer (BBC) treatment is a challenging case in radiation treatment due to its complexity, the wide area of the chest that must be irradiated and the overlap between the left and right breast dose distribution. New techniques were invented to reduce the adverse radiation effects and innovate the greater efficiency for the treatment.8–10 The monitor unit (MU) is a measure of the lineal accelerator deliverability. It can predict the output dose efficiency.11
This study aimed to using volumetric modulation arc therapy to analyze and evaluate the plans for patients with bilateral breast cancer who underwent left mastectomy and right lumpectomy with left regional lymph node dissection.
MethodsEleven female patients with synchronous bilateral breast cancer who underwent left-sided mastectomy with level I & II axillary lymph nodes dissection and right-sided lumpectomy were selected from the Baghdad Centre for Radiation Therapy and Nuclear Medicine, Medical City, Baghdad, Iraq. An experienced radiation oncologist delineated each patient. The contouring included the left breast and right chest wall as clinical target volume (CTVp) and level III and level IX lymph nodes regions as CTVn.12 1 cm margin had been added over CTVp to create PTVp and 7 mm margin had been added over CTVn to create PTVn. The planning technique was for VMAT with a single beam and 2 arcs. The angular positions started from 230° and ranged 140° clockwise and anticlockwise. The angles were separated by intervals of 20°. The treatment planning process was performed using the Monaco treatment planning system (TPS) version 5.1 and forwarded for treatment to a Synergy lineal accelerator manufactured by Elekta, Sweden. The isocenter point was positioned below the sternum, as shown in Fig. 1.
Evaluation toolsThe evaluation tools were obtained from dose-volume histogram (DVH) statistical analysis. The PTV values were measured at volumes that received at least 95%, 105%, and 110% of the prescribed dose, which were defined as measures for minimum and maximum doses.
The homogeneity index (HI) is characterized by the absorbed-dose distribution. The most common definition of HI is13,14:
where HI is the homogeneity index, D5% is the absorbed dose in 5% of the isodose line, D95% is the absorbed dose in 95% of the isodose line, and D50% is the absorbed dose in 50% of the isodose line.An HI value is zero indicates that the absorbed-dose distribution is almost homogeneous.14
The conformity index (CI) is a characterization of the dose for the high-dose region that conforms to the target volume (PTV). It is used to evaluate the conformal coverage of the PTV by the isodose of the prescribed volume in the treatment plan14,15:
where CI is the conformity index, VTV is the volume of the actual prescribed dose, VPTV is the volume of PTV, and TVPV is the volume of VPTV within VTV. Treatment conformity was defined as CI =1.The evaluation of OARs was performed by measuring the mean dose reaching the heart and lungs and the volume that received 2000 cGy from the prescribed dose (the volume receiving at least x cGy, which depends on the organ). The number of MU is obtained as a delivery parameter.
Statistical analysisThe simple data were analyzed using the statistical package of Statistical Packages for Social Sciences V24 (SPSS-24). Data are presented as the mean and standard deviation. The nonparametric Spearman's rho correlation was calculated as part of the data analysis.
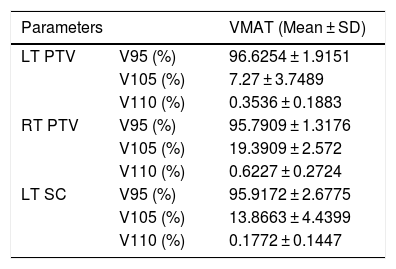
ResultsThe target coverage for the left and right primary sides as well as the left-sided regional lymph node results are illustrated in Table 1. From the results, it appears that the VMAT shows better coverage for the left mastectomy side than the right lumpectomy and a lower dose maximum to V105% and V110%, respectively. The left-sided regional lymph nodes showed good coverage and low doses of V105% and V110%, respectively.
Planning target volume coverage using VMAT treatment planning.
| Parameters | VMAT (Mean ± SD) | |
|---|---|---|
| LT PTV | V95 (%) | 96.6254 ± 1.9151 |
| V105 (%) | 7.27 ± 3.7489 | |
| V110 (%) | 0.3536 ± 0.1883 | |
| RT PTV | V95 (%) | 95.7909 ± 1.3176 |
| V105 (%) | 19.3909 ± 2.572 | |
| V110 (%) | 0.6227 ± 0.2724 | |
| LT SC | V95 (%) | 95.9172 ± 2.6775 |
| V105 (%) | 13.8663 ± 4.4399 | |
| V110 (%) | 0.1772 ± 0.1447 | |
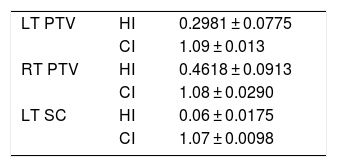
The homogeneity and conformity evaluation results for the plans are listed in Table 2. The statistics show that the VMAT technique gives a higher dose distribution homogeneity. A higher homogenous dose was obtained for the left regional lymph nodes, followed by the left PTVp and then the right PTVp. Higher conformity was obtained at the left PTVp, followed by the right PTVp and finally the PTVn.
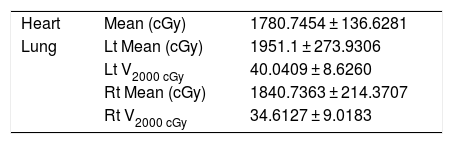
The resulting values for organs at risk are listed in Table 3.The organ at risk sparing terms studied included in this study are the mean dose to the heart and the mean dose for each lung volume that received 2000 cGy of the sparing dose. The recommended mean dose to the heart should not exceed 1600 cGy (16 Gy). The DVH statistics show that the dose exceeds the limits for the heart. The left lung was protected less than the right lung, but both remained within the limits.
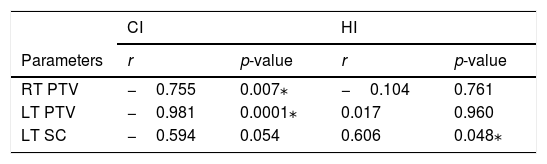
Monitor units and evaluation toolsThe mean ± standard deviation of the total number of monitor units (MU) is 1953.650 ± 429.572. The correlation between MUs and HI and CI of the VMAT plan is illustrated in Table 4. Correlations were found between the MU and CI for the left and right PTVs and the left supraclavicular region. Only left supraclavicular lymph nodes showed a correlation with MU. When the monitor unit increases conformity, the index also increases. As the monitor units increase, the homogeneity index decreases.
DiscussionBreast cancer widely affects female patients around the world.16,17 Synchronous bilateral breast cancer is rarely diagnosed in female patients around the world (approximately 2%).10,18 Previous studies have shown that when the number of beams increases, conformity may increase. The VMAT technique has an extreme example of using multiple beams in which the gantry is continuously treating while intensity modulated beams are being targeted to the PTV region. This VMAT technique is limited by the number of fields, thus improving the size of the target's low dose distribution.9
The accumulation of dose had a damaging effect on the heart and lungs during the radiation treatment fractions. In breast cancer, especially when patients undergo left-sided mastectomy, the main threat to the heart is an increased risk of diseases such as stenosis in the left descending artery (LAD), which may develop to the point of causing heart failure.19,20
The technique used in our study is the bi-tangential arc technique of VMAT delivery. This technique was the same one used by Munshi et al.,8 who reported that the mean heart dose was less than 3 Gy, a lower value than we obtained in our study. Other studies have attempted to improve the dose conformity by using full arc therapy and acquiring the best coverage and lower dose to OARs as the study included only the patients who underwent 3D CT simulation only rather than 4D simulation or ABC (Active Breathing Coordination). The mean lung dose in our study was higher than the dose reported in a study by Zurl et al.21
The monitor unit is considered a good prediction of the deliverability of the radiation. VMAT planning assesses high conformity for bilateral breast cancer with left-sided mastectomy and right-sided lumpectomy. Correlation analysis is a new idea for a dosimetric test. It shows an effective result and could be depended on as an evaluation tool. The medical physicist should be checking the total number of monitor units during the planning and make a balance to acquire high plan quality.
The use of the VMAT planning technique in bilateral breast cancer is crucial and depends on the laterality of the mastectomy. The start and end angles and the length of the arc are important and need to be precisely set during the planning process. The dose to the organs at risk can be increased if incorrect positioning is chosen. Some studies using VMAT take into consideration the supine or prone position of the breast during treatment.22–24
ConclusionThe treatment planning technique of volumetric modulation arc therapy (VMAT) shows qualified coverage for both breasts and regional lymph nodes in patients with simultaneous bilateral breast cancer. This technique provides high dose conformity and high homogenous dose distribution for the target. The correlation between the conformity index and the total number of monitor units is an accepted evaluation tool for this technique and can indicate the quality of radiation delivery.
FundingThis work has not received any funding.
Ethics approval and consent to participateNot applicable.