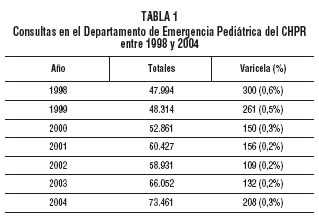
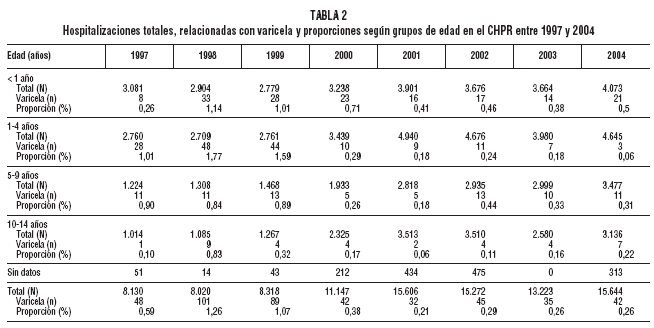
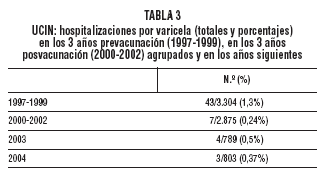
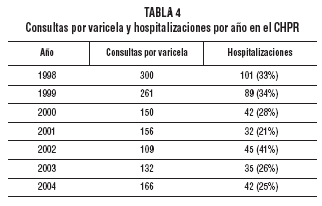
3 years after the introduction of routine varicella vaccination at 12 months of age. Material and methods. We analyzed the database and medical records of all outpatient visits and hospital admissions and those for varicella in the largest pediatric center in the country. Visits to the pediatric emergency department and hospital admissions to general wards and the pediatric intensive care unit (ICU) were analyzed. The prevaccination years studied were 1997-1999 (varicella vaccination began in October 1999). Varicella infection was diagnosed clinically. The vaccine used was Varilix (GSK). Results. In the 3 years after introduction of the vaccine there was a statistically significant reduction in outpatient visits, all hospital admissions, and admissions to the pediatric ICU compared with the 3 prevaccination years. The greatest reductions were found in the group aged 1-4 years, although there were also significant reductions in the group age 5-9 years and in infants under 12 months of age. There were no changes in the group aged 10-15 years. Conclusions. The high vaccination coverage achieved at 12 months of age (more than 90%) was accompanied by a significant reduction in outpatient visits and hospital admissions. The vaccination coverage achieved and the results obtained may be explained by the fact that vaccination is compulsory and free of charge.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora