La tormenta arrítmica (TA) es una situación de emergencia potencialmente letal, con una elevada tasa de mortalidad. Cuando el tratamiento convencional agudo es inefectivo, el bloqueo del ganglio estrellado puede ayudar a controlar la arritmia, aportando un bloqueo simpático cervicotorácico visceral. El objetivo de este estudio es valorar la efectividad y seguridad de los bloqueos del ganglio estrellado (BGE) para el tratamiento de la TA refractaria.
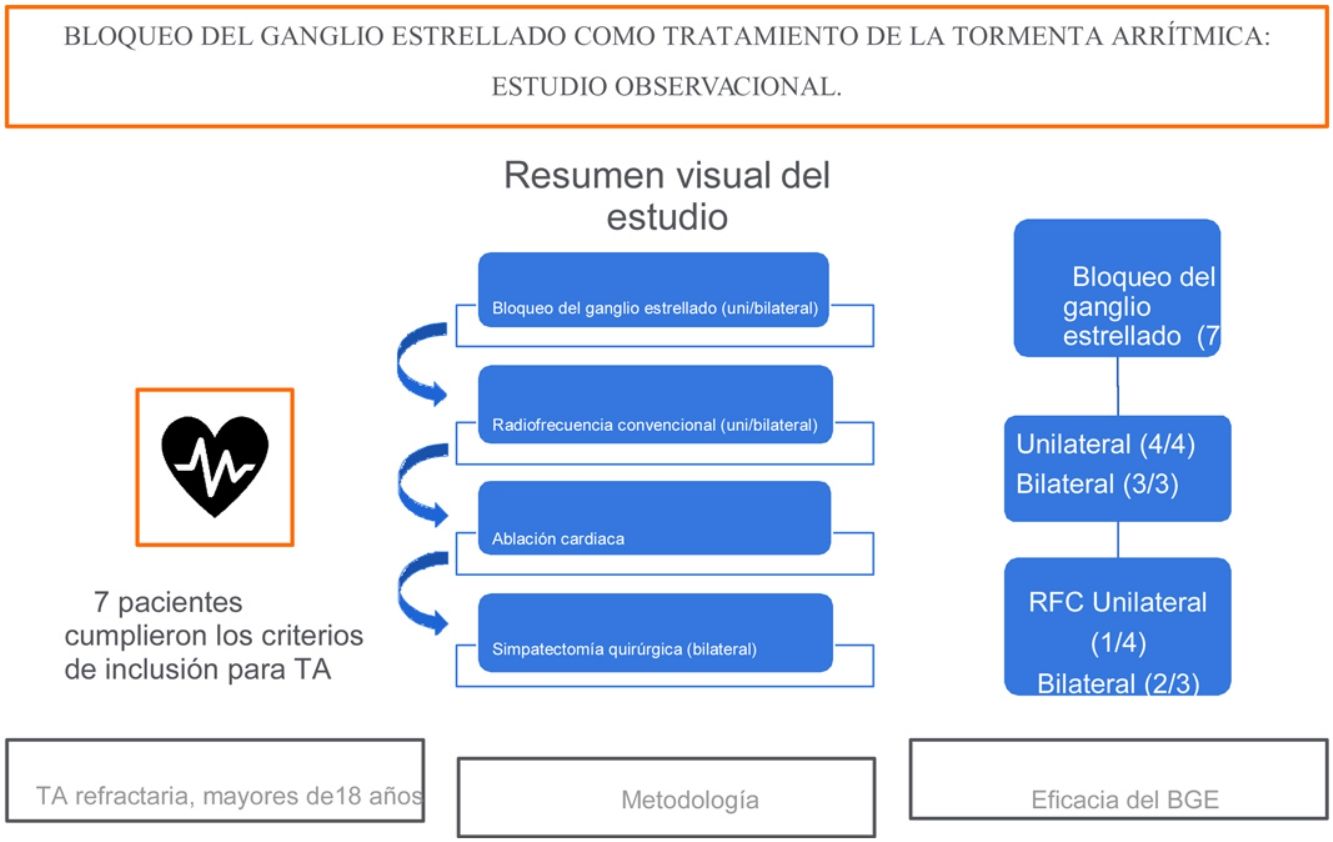
MétodoSeguimiento de una cohorte de pacientes con TA refractaria que cumplieron los criterios para la realización de BGE. Dicho bloqueo fue ecoguiado al nivel de C6, utilizando un anestésico y un esteroide, de manera unilateral izquierda en primer lugar, y bilateral de no existir respuesta, realizándose posteriormente ablación mediante radiofrecuencia (RFC) guiada por fluoroscopio en C7 de no existir respuesta favorable, sino recidiva subsiguiente.
ResultadosSe incluyeron siete pacientes, con una tasa de mortalidad durante el ingreso de 14,29%. Cuatro pacientes recibieron bloqueos unilaterales del ganglio estrellado, y en tres pacientes se realizaron bloqueos bilaterales. En seis de ellos se aplicó ablación, y uno de ellos tenía implantado un cardioversor-desfibrilador. La TA fue controlada temporalmente, más allá del efecto del anestésico local en todos los pacientes. Tres de ellos recibieron ablación por RFC, y dos simpatectomías torácicas quirúrgicas. El único efecto secundario fue el síndrome de Horner, que se observó en todos los casos tras realizar el bloqueo del ganglio estrellado con anestésico local. Dos pacientes murieron tras recibir el alta, y cuatro siguen en sus casas, tres de ellos sin haber sido ingresados a causa de episodios ventriculares durante más de dos años.
ConclusiónEl bloqueo ecoguiado del ganglio estrellado es una técnica efectiva y segura para el tratamiento de la TA refractaria, como complemento del tratamiento cardiológico habitual.
Arrhythmic storm is a life-threatening emergency with a high mortality rate. When acute conventional treatment is ineffective, a stellate ganglion block can contribute to the control of the arrhythmia by providing a visceral cervicothoracic sympathetic block. The objective of the study is to assess the effectiveness and safety of stellate ganglion blocks for the treatment of refractory arrhythmic storm.
MethodFollow-up of a cohort of patients with refractory arrhythmic storm that met the criteria for performing stellate ganglion blocks. The block was ultrasound-guided at C6-level using local anaesthetic and a steroid, left unilateral first, bilateral if no response, and followed by fluoroscopy-guided radiofrequency ablation at C7 if there was a favourable response but subsequent relapse.
ResultsSeven patients were included, with a mortality rate during admission of 14.29%. Four patients received unilateral and three bilateral stellate ganglion blocks. Six were ablated and one of them had an implanted cardioverter-defibrillator. Arrhythmic storm was controlled temporarily beyond the effect of the local anaesthetic in all patients. Three underwent radiofrequency ablation and two underwent surgical thoracic sympathectomy. The only side effect was Horner's syndrome, which was observed in all cases after administering a stellate ganglion block with local anaesthetic. Two died after discharge and four are still at home, three of them without further admission due to ventricular events for more than two years.
ConclusionAn ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block is an effective and safe technique in the treatment of refractory arrhythmic storm as a complement to the usual cardiological treatment.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora