El objetivo de este estudio fue evaluar el efecto de diferentes dosis de carga de dexmedetomidina (formulación Dexdor®) en el tiempo para lograr y mantener un nivel óptimo de sedación, y su repercusión hemodinámica.
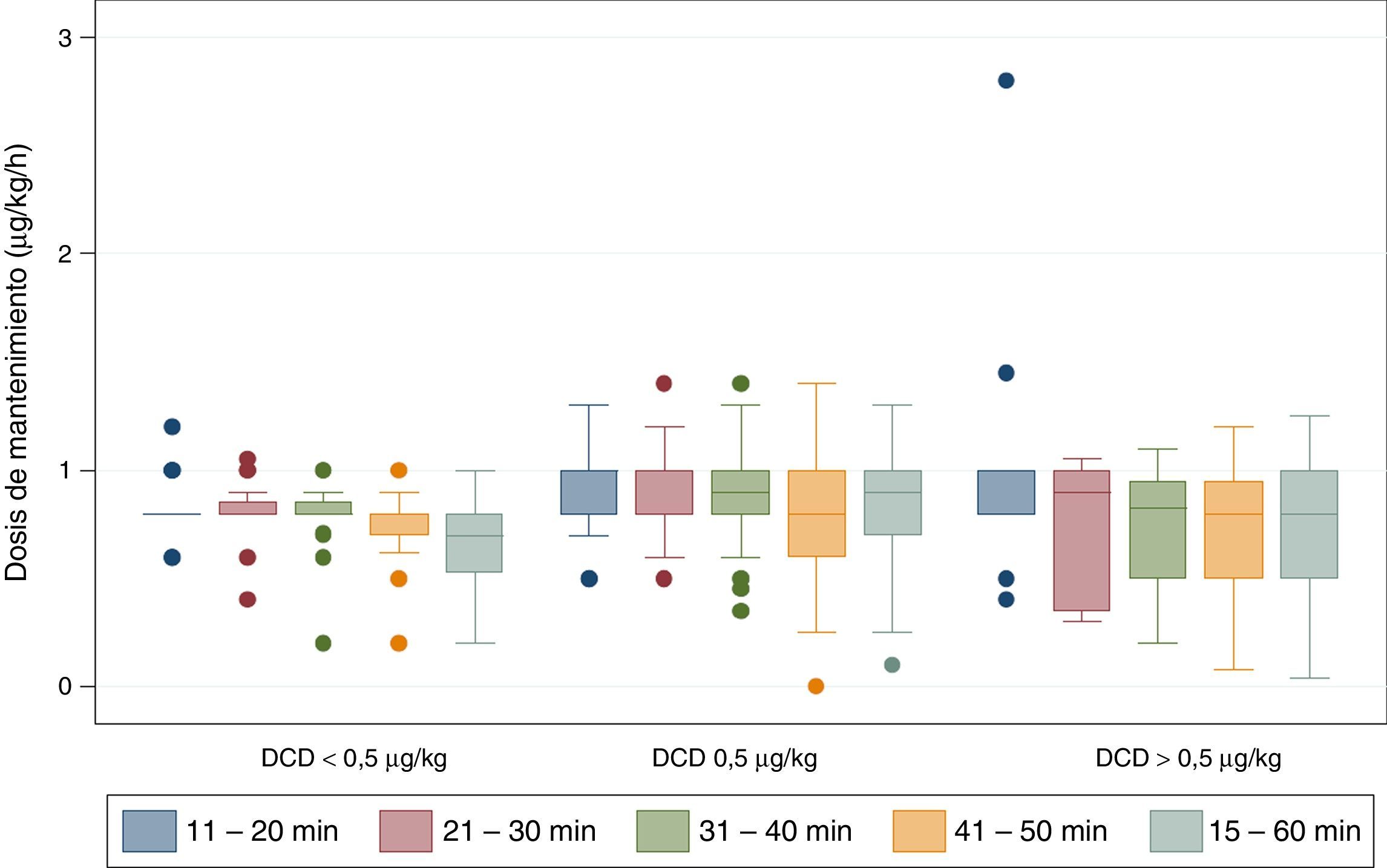
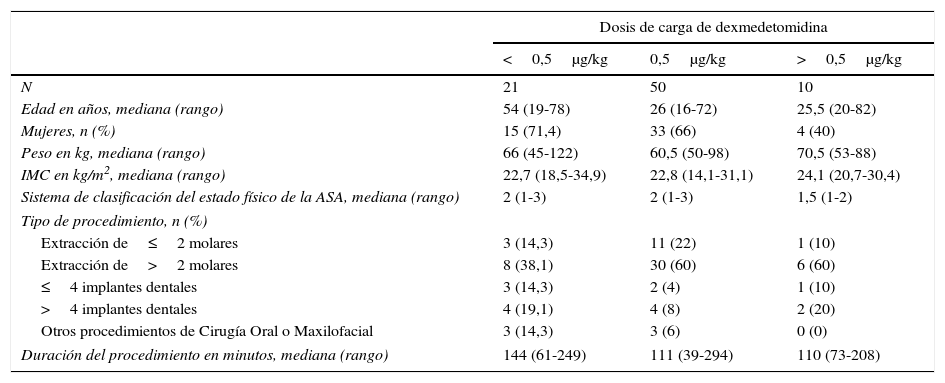
Material y métodosEstudio observacional aprobado por el CEIC-Navarra en pacientes programados para cirugía oral y maxilofacial ambulatoria con dexmedetomidina en la Clínica Universidad de Navarra entre febrero de 2013 y noviembre de 2014. En función de la dosis de carga los pacientes fueron agrupados en 3 categorías:<0,5; 0,5; y>0,5μg/kg. El nivel óptimo de sedación se definió como un índice biespectral<85. Los datos se analizaron utilizando técnicas de análisis de supervivencia. Los requerimientos de fármacos vasoactivos fueron evaluados mediante regresión logística exacta.
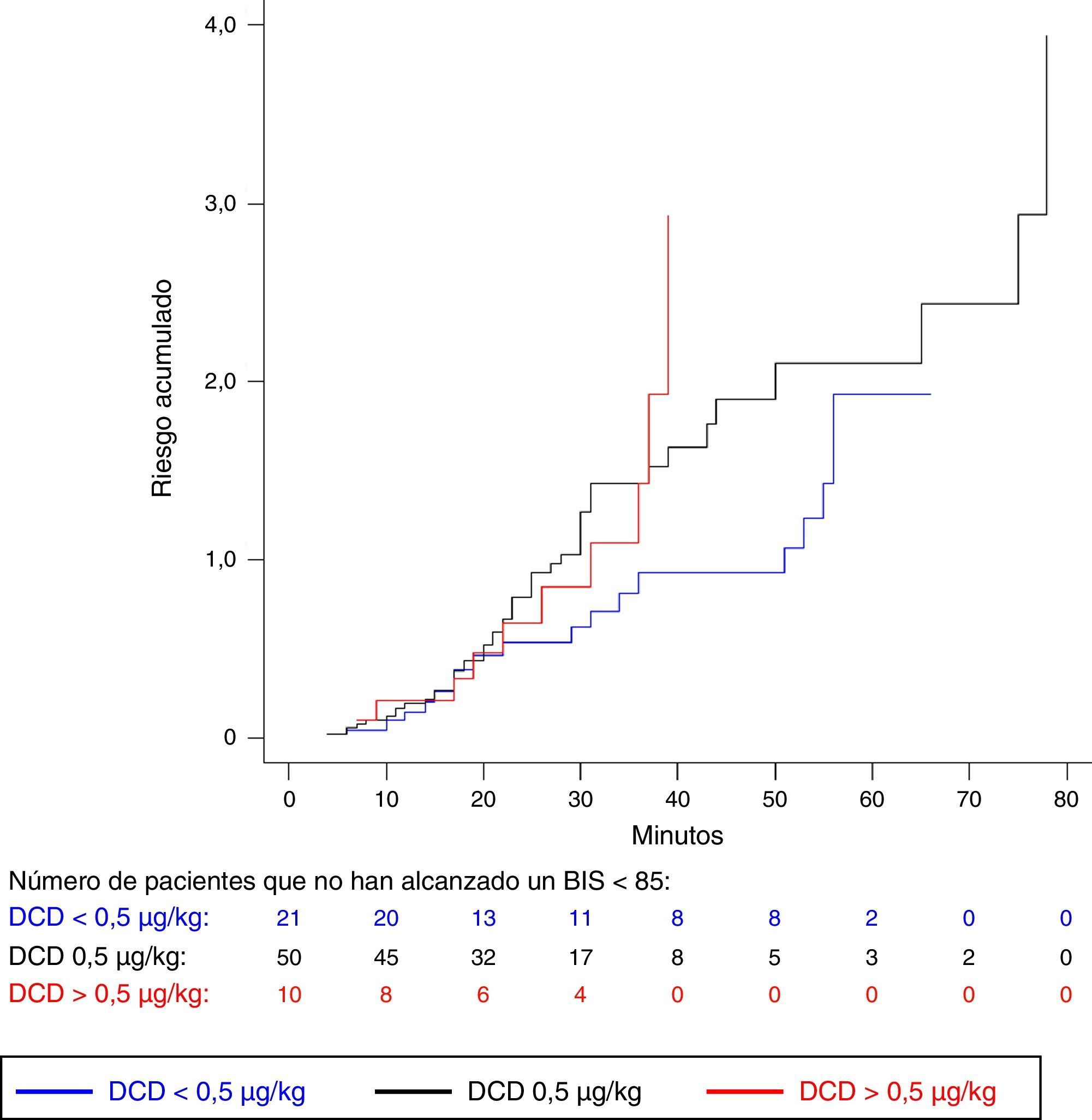
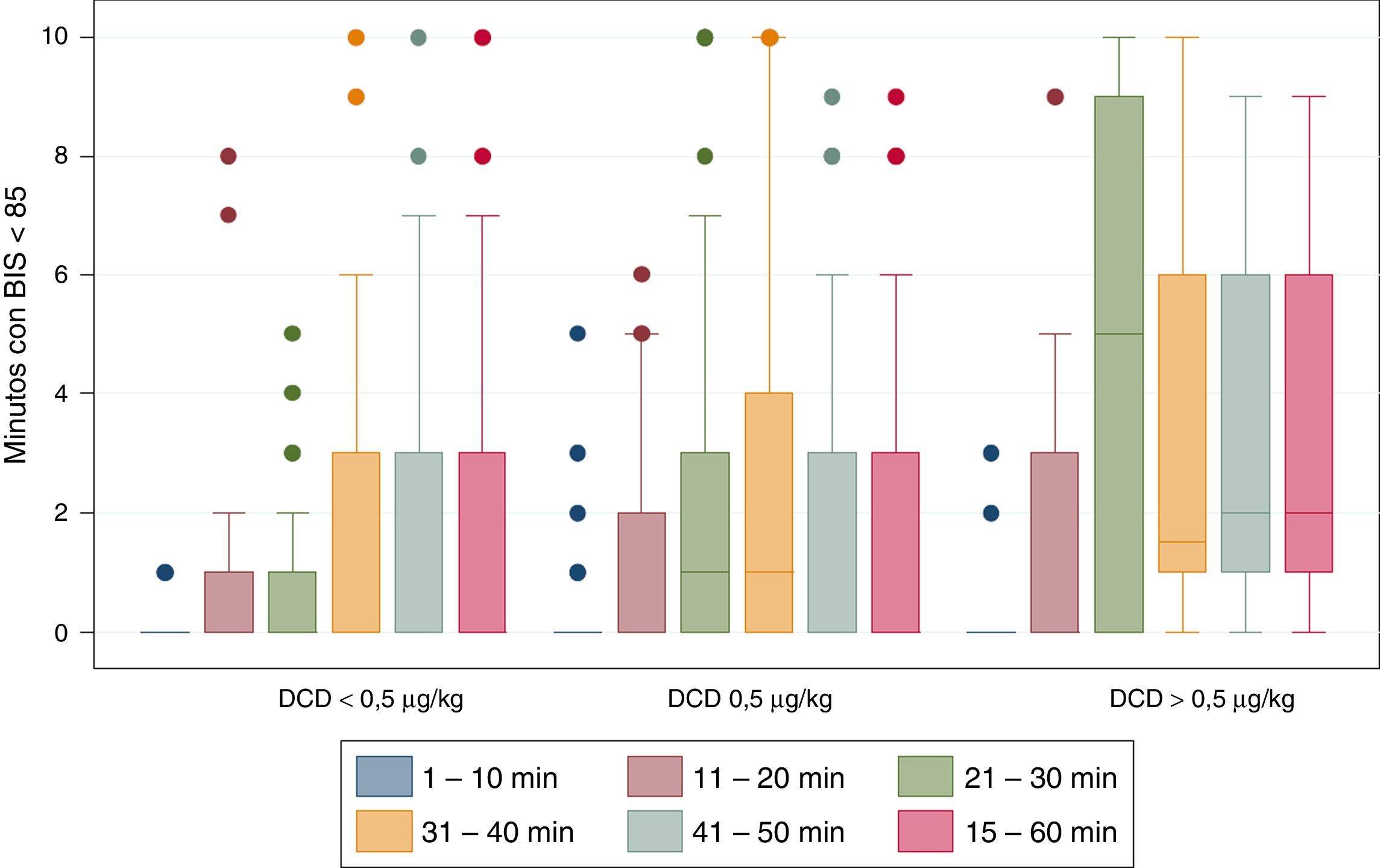
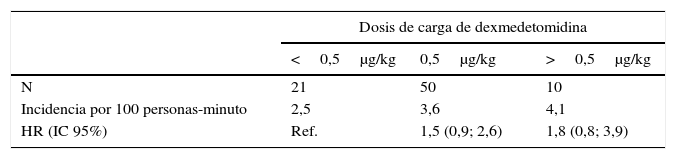
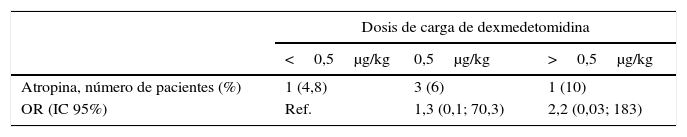
ResultadosOchenta y un pacientes fueron evaluados. La hazard ratio de alcanzar un índice biespectral<85 para los pacientes de los grupos de 0,5 y>0,5μg/kg fue de 1,5 (IC 95% 0,9; 2,6) y 1,8 (IC 95% 0,8; 3,9), respectivamente, en comparación con el grupo inferior. Cinco pacientes (6,2%) precisaron de atropina. Los pacientes en el grupo de>0,5μg/kg mostraron mayor riesgo de requerir atropina respecto al grupo de<0,5μg/kg (odds ratio 2,2; IC 95% 0,03; 183).
ConclusiónUna dosis de carga de Dexdor®>0,5μg/kg parece reducir el tiempo necesario para alcanzar y mantener un nivel óptimo de sedación durante los primeros 60min de procedimiento. La posible relación entre la dosis de carga y los requerimientos de atropina precisa una investigación más exhaustiva.
Dexdor® do not include the possibility of loading dose, which could increase time to achieve adequate sedation for ambulatory procedures. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of several loading dose of dexmedetomidine in the time to achieve and maintain an optimal level of sedation and its clinical hemodynamic repercussion.
Material and methodsThe IRB approved this observational study for patients that underwent oral and maxillofacial ambulatory surgery under dexmedetomidine at the University of Navarra Clinic from February 2013 to November 2014. According to the loading dose the patients were grouped into 3 categories:<0.5, 0.5, and>0.5μg/kg. Optimal level of sedation was defined as bispectral index<85. Data were analyzed using survival analysis techniques. Vasoactive drugs requirements was evaluated using exact logistic regression.
ResultsEighty-one patients were evaluated. Hazard ratios for patients in 0.5 and >0.5μg/kg loading dose categories for achieving a bispectral index<85 were 1.5 (95% CI 0.9, 2.6) and 1.8 (95% CI 0.8, 3.9), respectively, compared with the lowest category. Five patients (6.2%) required atropine for bradycardia. Patients in the group>0.5μg/kg showed greater risk of requiring atropine compared with the group<0.5μg/kg (odds ratio 2.2; 95% CI 0.03, 183).
ConclusionLoading dose of dexmedetomidine>0.5μg/kg appears minimize the time to achieve and maintain an optimal level of sedation during the first 60min of procedure. Further investigation to elucidate the association between loading dose of dexmedetomidine and subsequent atropine requirements may be warranted.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora