Durante los últimos 50 años la fluidoterapia de mantenimiento para pacientes pediátricos se ha realizado con soluciones hipotónicas y se ha cuantificado mediante la fórmula de Holliday y Segar. Recientes publicaciones han puesto de manifiesto tanto la incidencia como la morbi-mortalidad asociadas a la hiponatremia postoperatoria, generando opiniones encontradas sobre la idoneidad de la fluidoterapia perioperatoria, tanto respecto a su cantidad como a su calidad.
Describimos tres casos de encefalopatía hiponatrémica en niños, tras intervenciones menores realizadas por diferentes servicios quirúrgicos en nuestro centro.
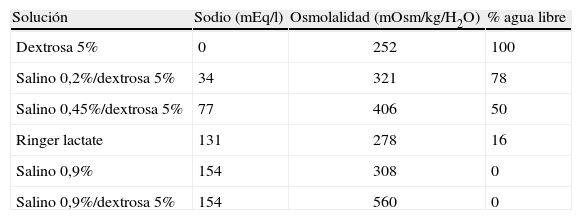
La disminución en la capacidad de excreción renal de agua libre perioperatoria condiciona de forma marcada la fluidoterapia a realizar durante este periodo; a pesar del reconocimiento de este hecho, existe gran controversia respecto a la fluidoterapia pediátrica ideal que no podrá resolverse hasta que no se realicen amplios ensayos clínicos, prospectivos y randomizados comparando la fluidoterapia de mantenimiento con soluciones hipotónicas e isotónicas. Sin embargo, es posible realizar unas recomendaciones generales para reducir la incidencia y consecuencias de esta alteración electrolítica.
Fluid replacement therapy for pediatric patients in the past 50 years has meant the infusion of hypotonic solutions in amounts calculated using the Holliday-Segar formula. Recent studies have focused attention on the incidence of postoperative hyponatremia and associated morbidity and mortality rates, generating debate on the advisability of perioperative fluid therapy and calling into question both the effectiveness of this strategy and the quantities used. We report 3 cases of hyponatremic encephalopathy in children following different types of minor surgery. Free water excretion by the kidneys is known to be a conditioning factor in this therapy, yet the ideal way to provide pediatric fluid therapy is still hotly debated. The question cannot be resolved until large randomized clinical trials are carried out to compare the use of hypotonic and isotonic solutions. Some general recommendations can be offered, however, in the interest of lowering the incidence of electrolyte disturbances and diminishing their repercussions.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora