Demostrar la eficacia del bloqueo de los nervios digitales (BND) para mejorar la oximetría de pulso (OP) en condiciones de baja perfusión hística.
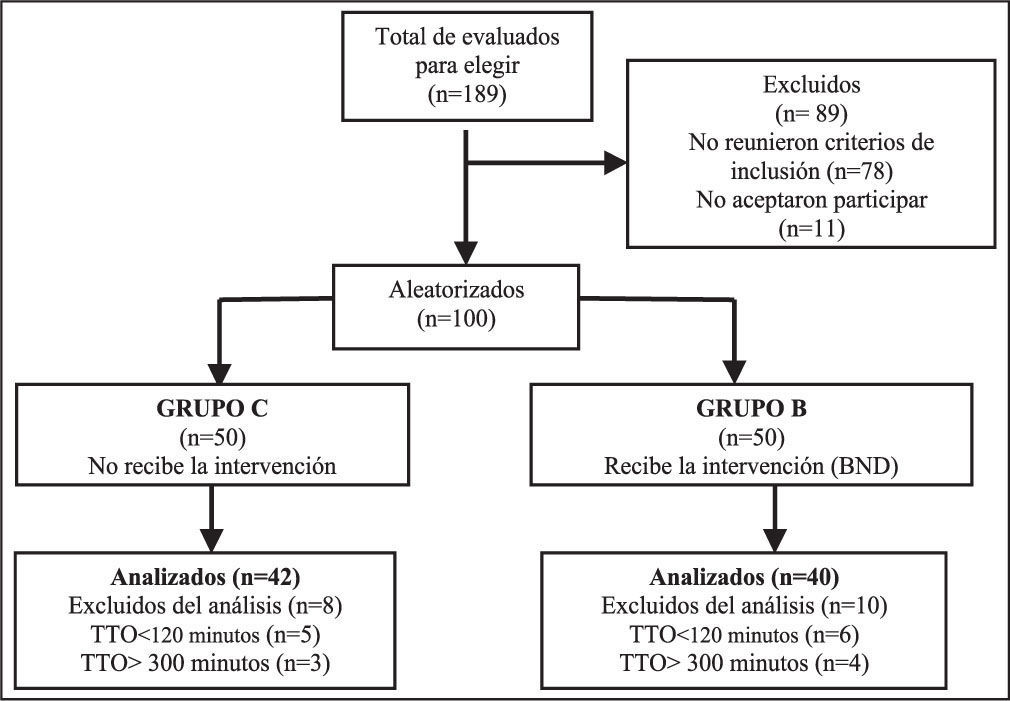
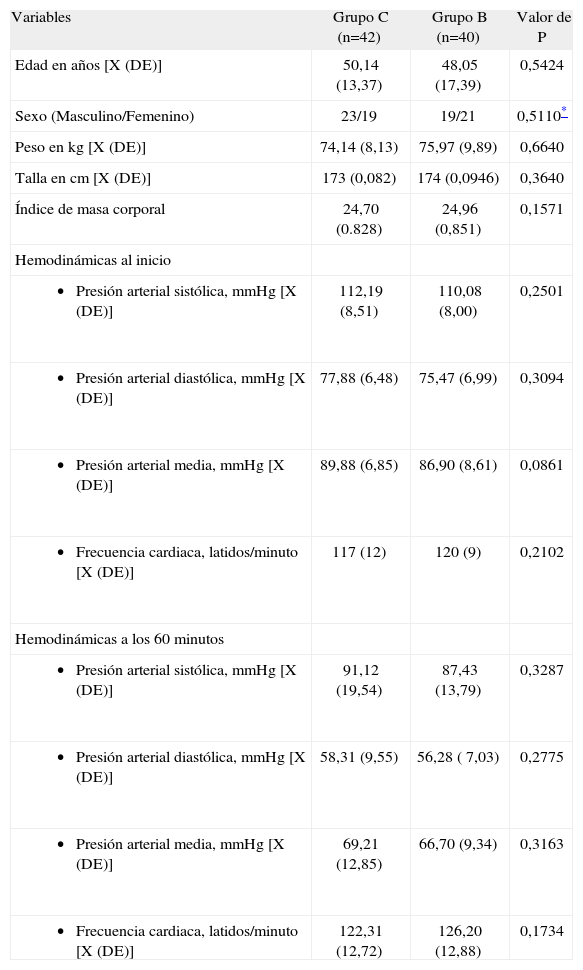
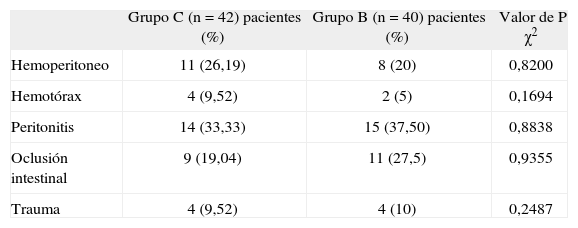
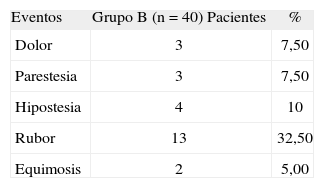
MétodoPacientes adultos operados por afecciones caracterizadas por hipoperfusión, conducidos con anestesia general, de forma aleatoria y con registros a simple ciego. Se asignaron a dos grupos: Grupo C (control) y grupo B (experimental). El grupo B recibió un BND en el dedo medio de la mano izquierda donde se colocó el sensor con límites de tiempo entre 120 y 300 minutos. Se registraron: edad, sexo, diagnóstico, tiempo total de observación (TTO), porcentajes de tiempo con OP no disponible (OPnodisp) y porcentaje de tiempo con OP inestable (OPinest). Entre 16 y 24 horas después de terminada la intervención se interrogó y examinó a cada paciente en busca de rubor, parestesias, hipostesia, dolor y equimosis. Para las variables dicotómicas o nominales se empleó la prueba χ2 y para comparar las medias de edad, TTO, OPnodisp, y OPinest, la prueba t de Student. En ambos casos con un nivel de significación de 0,05.
ResultadosSe asignaron 50 pacientes a cada grupo. Un total de 82 enfermos permanecieron en el ensayo (C=42 y B=40). No hubo diferencias significativas en cuanto a diagnósticos ni TTO. En el grupo C los porcentajes de tiempo promedio con OPnodisp y OPinest fueron superiores (11,1% vs. 4,4% y 35,9% vs. 15,7%; respectivamente), p<0,001.
ConclusiónEl BND es una alternativa para evitar las fallas de OP en condiciones de baja perfusión periférica.
To demonstrate the efficacy of a digital nerve block for improving pulse oximetry in conditions of low tissue perfusion.
MethodA randomized single-blind study of adult patients undergoing surgery under general anesthesia for conditions characterized by hypoperfusion. Patients were assigned to a control group or an experimental group. The experimental group received a digital nerve block in the middle finger of the left hand; a sensor was then placed on the finger for between 120 and 300 minutes. Age, sex, diagnosis, total observation time (TOT), percentage of time with no pulse oximeter signal (NoPO), and percentage of time with an unstable pulse oximeter signal (UnstPO) were recorded. Each patient was questioned between 16 and 24 hours after surgery and was examined for flushing, paresthesia, hypoesthesia, pain, and ecchymosis. The χ2 test was used to compare dichotomized or nominal variables and the t test was used to compare age, TOT, NoPO, and UnstPO. Values of P<.05 were considered statistically significant in both cases.
ResultsFifty patients were randomized to each group. A total of 82 patients remained in the study (control group=42, experimental group=40). There were no significant between-group differences in diagnoses or TOT. The mean values for NoPO and UnstPO were higher in the control group than in the experimental group (11.1% vs 4.4% and 35.9% vs 15.7%, respectively; P<.001).
ConclusionA digital nerve block can be used to prevent pulse oximetry failures in conditions of low peripheral perfusion.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora