Evaluar la utilidad y seguridad del remifentanilo para el control hemodinámico en cesáreas de pacientes de alto riesgo no susceptibles de anestesia espinal.
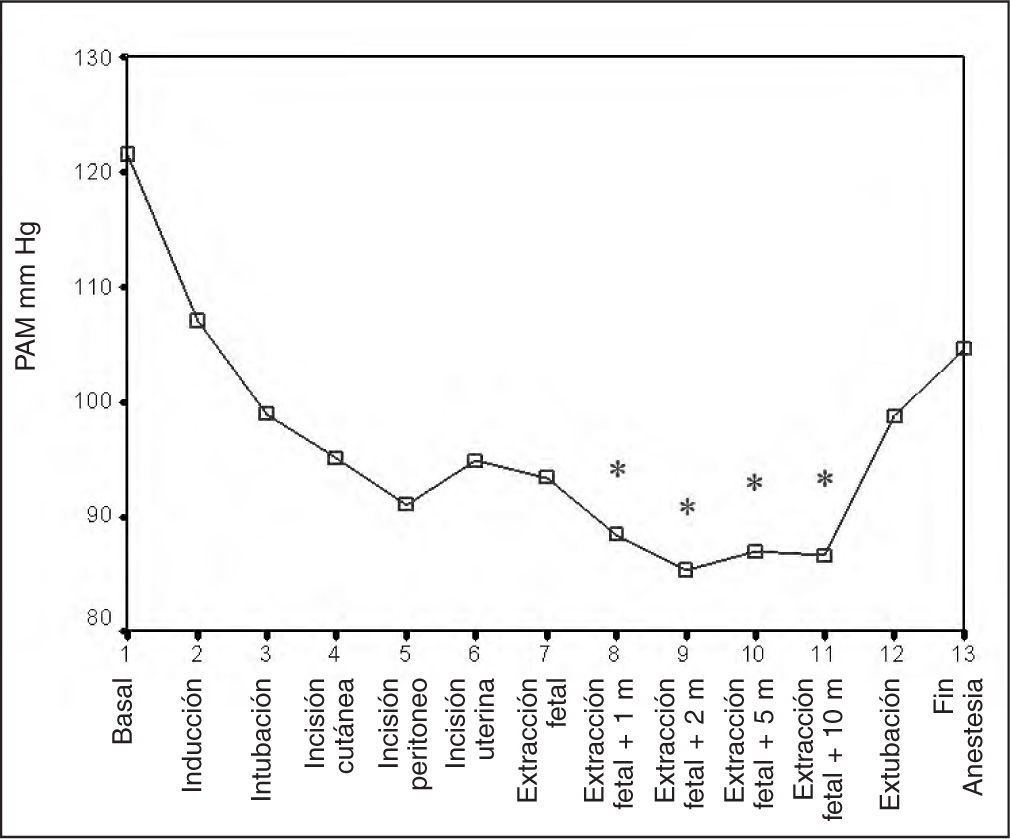
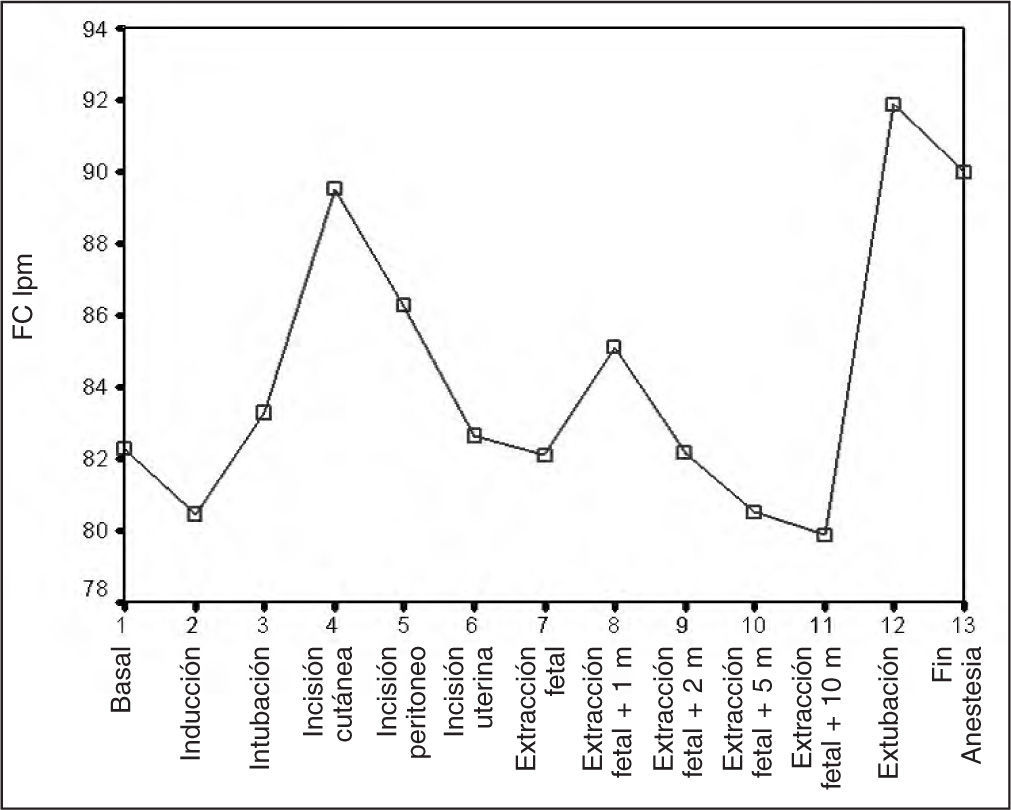
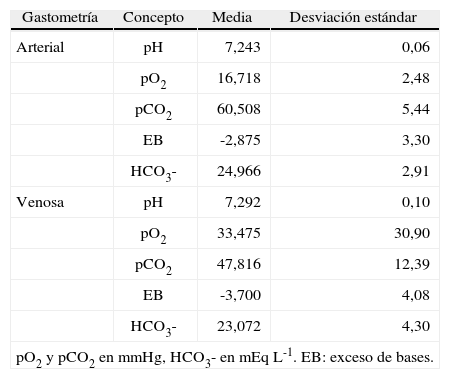
MétodosUn minuto antes de la inducción administramos un bolo de 1μg kg-1 de remifentanilo, después, propofol (2,5mg kg-1), succinilcolina (1mg kg-1), cisatracurio, sevoflurano-O2 - N2O y 5μg kg-1 de fentanilo tras la ligadura del cordón. Registramos los valores hemodinámicos maternos, pulsioximetría, capnografía, índice biespectral, presencia de rigidez muscular. En el neonato valoramos el bienestar fetal, peso y necesidad de naloxona. Consideramos estabilidad hemodinámica cuando la presión arterial no variaba más del 15% respecto al basal.
ResultadosIncluimos 12 pacientes con indicación quirúrgica por abruptio placentae, hemorragia subaracnoidea, síndrome HELLP y preeclampsia. Observamos resultados concordantes con estabilidad hemodinámica en todas las pacientes durante la cirugía. Ningún neonato presentó rigidez ni necesitó naloxona. El test de Apgar al minuto fue 6,42±1,5 y 8,42±0,9 a los 5 min.
ConclusiónEl remifentanilo en bolo de 1μg kg-1 puede ser útil en el control hemodinámico materno de la paciente obstétrica de alto riesgo. Ante el riesgo de depresión neonatal, es conveniente seleccionar los casos donde se utilice, y disponer de medios de reanimación neonatal.
To evaluate the utility and safety of remifentanil for hemodynamic control during cesarean section in high-risk patients ineligible for spinal anesthesia.
MethodsOne minute before induction we injected a bolus of 1μg·kg-1 of remifentanil, followed by propofol (2.5mg·kg-1), succinylcholine (1mg·kg-1), cisatracurium, sevoflurane in oxygen and nitrous oxide, and fentanyl (5μ g·kg-1) after clamping the umbilical cord. We recorded maternal hemodynamic variables, pulse oximetry, capnography, bispectral index, and presence of muscular rigidity. In the neonate we assessed fetal wellbeing, weight, and requirement for naloxone. Hemodynamic stability was defined as no more than 15% variation in arterial pressure with respect to baseline.
ResultsTwelve patients undergoing surgery because of placenta abruptio, subarachnoid hemorrhage, HELLP syndrome, or preeclampsia were enrolled. Hemodynamic variables were consistently stable during surgery in all patients. No cases of neonatal rigidity were noted and there was no need for naloxone. The mean Apgar score was 6.42 (1.5) at 1 minute and 8.42 (0.9) at 5 minutes.
ConclusionBolus injection of 1μg·kg-1 of remifentanil may be useful for maintaining maternal hemodynamic stability in high-risk obstetric cases. Given the risk of neonatal depression, this resource should be used selectively and the means for neonatal resuscitation should be available.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora