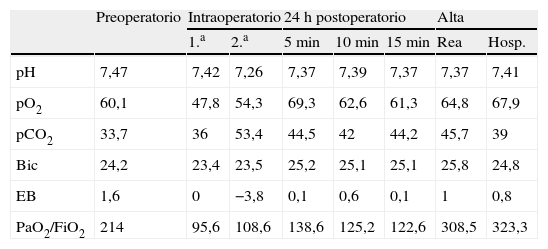
El diagnóstico y tratamiento de la insuficiencia respiratoria es parte de la práctica diaria del anestesiólogo, y la hipoxemia una de sus consecuencias fisiológicas y analíticas. Pacientes con una leucocitosis extrema secundaria a leucemia pueden sufrir un diagnóstico incorrecto de hipoxemia, llamada «seudohipoxemia». Esto se debe fundamentalmente al rápido consumo de oxígeno in vitro, y se caracteriza por una presión arterial de oxígeno (PaO2) baja a pesar de tener una saturación de oxígeno (SpO2) normal medida por pulsioximetría. La seudohipoxemia se presenta en pacientes con trombocitosis o hiperleucocitosis por crisis blástica de una leucemia. Se debe sospechar en pacientes con una discrepancia entre la SpO2 medida por oximetría de pulso y la PaO2. En este contexto, el pulsioxímetro es el método más útil para establecer el diagnóstico y evitar actuaciones innecesarias. Presentamos el caso de un paciente con leucemia mieloide crónica y extrema leucocitosis, intervenido de urgencia y diagnosticado de seudohipoxemia durante el período perioperatorio que conllevó un retraso en su extubación.
The diagnosis and treatment of respiratory failure is a part of the anaesthesist's daily practice, as well as the hypoxaemia that is one of its physiological and analytical consequences. Patients with an extreme leucocytosis secondary to leukaemia can suffer an incorrect diagnosis of hypoxemia, called “pseudohypoxaemia”. This is basically due to the rapid in vitro oxygen consumption, and is characterized by a low partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (PaO2) despite a normal oxygen saturation (SpO2) measured by pulse oximetry. Pseudohypoxaemia appears in patients with thrombocytosis or hyper-leucocytosis occurring during blastic crisis of a leukaemia. It must be suspected in patients with a discrepancy between the SpO2 measured by oximetry and the PaO2. In this context, pulse oximetry is the most accurate way to establish the diagnosis and to avoid unnecessary actions. We report the case of a patient with chronic myeloid leukaemia and extreme leucocytosis requiring emergency surgery, and diagnosed with pseudohypoxaemia during the perioperative period that led to a delay in the extubation of the patient.
Artículo
Comprando el artículo el PDF del mismo podrá ser descargado
Precio 19,34 €
Comprar ahora