113 - IMPACT OF INFLAMMATORY BURDEN ON EFFICACY OF UPADACITINIB MAINTENANCE THERAPY IN ULCERATIVE COLITIS: RESULTS FROM THE PHASE 3 U-ACHIEVE STUDY
1Robarts Research Institute, University of Western Ontario, London, Ontario, Canada. 2Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, NY, USA. 3Division of Gastroenterology, Surgical Department, Hospital Beatriz Angelo, Loures, Portugal. 4Division of Gastroenterology, Hospital da Luz, Lisbon, Portugal. 5Departments of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo, Japan. 6AbbVie Inc., North Chicago, Illinois, USA. 7University of Lyon, Saint-Etienne, France. 8Complejo Hospitalario de Navarra, Pamplona.
Introduction: Upadacitinib (UPA) is an oral selective and reversible Janus kinase inhibitor. Data are limited on the impact of inflammatory burden on the efficacy of the two maintenance doses of UPA (30 mg and 15 mg once daily [QD]).
Methods: The primary efficacy analysis of U-ACHIEVE Maintenance included the first 451 patients who achieved a clinical response after 8 weeks of UPA 45 mg QD treatment. The primary endpoint was clinical remission per Adapted Mayo score at week (wk) 52 and a key secondary endpoint was endoscopic improvement at wk 52. This post hoc analysis evaluated the efficacy, based on these endpoints, of UPA 30 mg vs. UPA 15 mg maintenance therapy in patients in U-ACHIEVE Maintenance stratified by three measures of inflammatory burden: baseline Full Mayo score > 9 vs. ≤ 9, presence of pancolitis (yes vs. no), and presence of ≥ 1 extraintestinal manifestation (yes vs. no).
Results: Both UPA 30 mg and UPA 15 mg demonstrated favorable efficacy compared with PBO, regardless of the inflammatory burden. However, the differences in proportions of responders who achieved clinical remission at wk 52 with UPA 30 mg vs. UPA 15 mg were greater in patients with a high inflammatory burden (difference: 12.0 -22.0%) than those without high inflammatory burden (difference: 1.4-6.2%). Similar results were seen for endoscopic improvement at wk 52 (high inflammatory burden [difference: 12.0-26.1%] relative to those without high inflammatory burden [difference: 0.2-14.1%]).
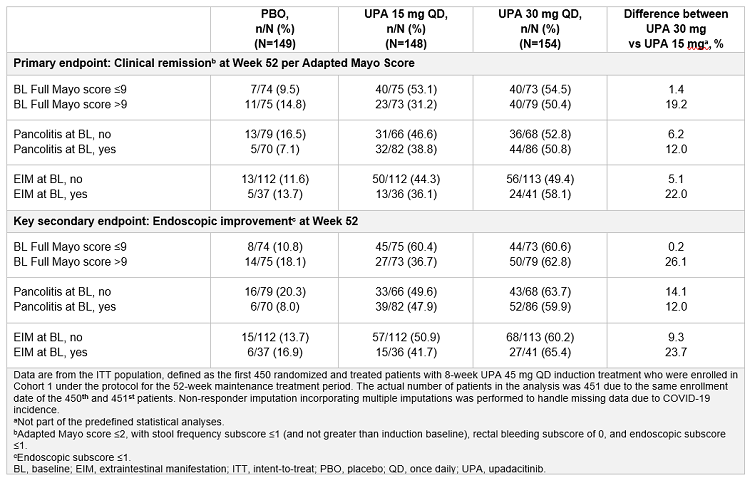
Conclusions: Both UPA maintenance doses were efficacious compared with PBO, regardless of inflammatory burden, in the achievement of clinical remission and endoscopic improvement. Although results should be interpreted with respect to the small sample size in some subgroups and the post hoc nature of the analysis, these data suggest that patients with a high inflammatory burden of UC may have a relatively greater benefit from UPA 30 mg than UPA 15 mg, compared with those without high inflammatory burden.









